Abstract
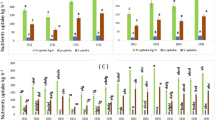
Nine cultivars of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) were grown in a soil poor in available N or P. There was clearly genetic variation of characteristics indicative of VA mycorrhiza-dependent phosphate mobilisation, namely, VA mycorrhiza fungal spore count (SC), percentage of infection (IF) by VA mycorrhizal fungi (VAMF) and acid and alkaline phosphatase activities. Among the cultivars, one was non-nodulating with low values for all characteristics and in another experiment, this non-nodulating cultivar, one of its parents (PI 259747), a national check (Robut 33-1) and the highest yielding cultivar among the original nine (NFG 7), were grown and investigated for various P-mobilising properties and yield. The linear regression coefficient of pod yield on % VAMF infection was significant in both the experiments. Additionally, many of the correlation coefficients of pod yield and VAM dependent characteristics were positive and significant. From consideration of published evidence, it seems possible to breed for the desirable reinforcing effects of infestation, by VAMF and Rhizobium that can ultimately improve the productivity of groundnuts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bethlenfalvay GJ, Pacovsky R S, Bayne H G and Stafford A E 1982 Interactions between nitrogen fixation, mycorrhizal colonisation and host plant growth in the Phaseolus-Rhizobium-Glomus symbiosis. Plant Physiol. 70, 446–450.
Daft M J and El-Giahmi A A 1976 Effct of Glomus infection on three legumes.In Endomycorrhizae. Eds. F E Sanders, B Mosse and P B Tinker. pp 581–592. Academic Press, London, New York.
Daft M J and Nicolson T H 1966 Effect of endogone mycorrhiza on plant growth. New Phytol. 65, 343.
Gerdemann J W and Nicolson T H 1963 Spores of mycorrhizalEndogone Species extracted from soil by wet sieving and decanting. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 46, 235–244.
Gianinazzi-Pearson V and Gianinazzi S 1976 Enzymatic studies on the metabolism of vescular-arbuscular mycorrhiza. I. Effect of mycorrhiza phosphorus nutrition on soluble phosphatase activities in onion roots. Physiol. Veg. 14, 833–841.
Krishna K R and Bagyaraj D J 1982 Influence and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza on growth and nutrition ofArachis hypogaea. Legume Res. 5, 18–22.
Krishna K R, Bagyaraj D J and Papavinasasundaram K G 1983 Acid and alkaline phosphatase activities in mycorrhizal and uninfected roots ofArachis hypogaea L. Ann. Bot. 51, 551–553.
Krishna K R, Shetty K G, Dart P J and Andrews D J 1984 Plant genotype-dependent differences in mycorrhizal colonisation rates. Proc. 6th North Am. Conf. Mycorrhizae, Bend, Oregon, USA, 402 p.
Phillips J M and Hayman D S 1970 Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 55, 158–161.
Tinker P B 1982 Mycorrhizae: The present situation.In Weather Soil Research Transactions of the 12th International Congress of Soil Science. pp 150–166, New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, P.S.K., Tilak, K.V.B.R. & Arunachalam, V. Genetic variation for VA mycorrhiza-dependent phosphate mobilisation in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Soil 122, 137–142 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02851921
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02851921