Abstract
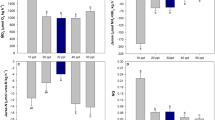
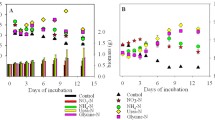
The energy budget ofBellamya earuginosa in a shallow algal lake, Houhu Lake (Wuhan, China) was investigated by the measurement of flesh production (32.8 kJ/(m2·a)), egestion (337.7 kJ/(m2·a)), metabolism (246.7 kJ/(m2·a)), and estimation of excretion (21.4kJ/(m2·a)). The net growth efficiency of the species is about 10.9%, which accords with the generally reported value for gastropods. In addition, the relationships between starvation respiration (R, mgO2/(Ind·d)), body weight (Wd, mg in dry wt) and temperature (T, °C) were also determined. The regression equationR=0.044Wd 0.537 e 0.061T was obtained by the least square method, The measured SDA of the species is 26.51% of its gross metabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apley, M. L., Russell-Hunter, W. D., Avolizi, R. J., 1967. Annual reproduction turnovers in the salt marsh pulmonate snail,Melampus bideniatus.Biol. Bull. 133: 455–456.
Avolizi, R. J., 1970. Biomass turnover in natural populations of viviparous sphaeriid clams: interspecific and intraspecific comparisons of growth, fecundity, mortality and biomass production. Ph. D. Dissertation, Syracuse Univ. Syracuse, 150 p.
Burky, A. J., 1968. Biomass turnover, energy balance and inter population variation in the stream limpet,Ferrissia rivularis (Say), with special reference to respiration, growth and fecundity. Ph. D. Dissertation. Syracuse Univ., Syracuse. 115 p.
Chen Qiyu, 1987. A preliminary study on the population dynamics and annual production ofBellamya aeruginosa (Reeve) in Donghu Lake, Wuhan.Acta Hydrobiol. Sinica 11(2): 117–130. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Comita, G. W., 1964. The energy budget ofDiaptomus siciloides Lilljeborg.Verh. Int. Ver. Limnol. 15: 646–653.
Deslous-Paoli, J. M., Boromthanarat, S., Heral, M., et al., 1990. Energy budget of aMytilus edulis L. Population during its first year on bouchots in the bay of Marennes-Oleron.Aquaculture 91(1990): 49–63.
Gardner, W. S., Nalepa, T. S., Slavens, D. R. et al., 1983. Patterns and rates of nitrogen release by benthos Chironomidae and Oligochaeta.Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 40(3): 259–266.
Gillespie, D. M., 1969. Population studies of few species of molluses in the Madison River, Yellowstone National Park.Limnol. Oceanogr. 14: 101–114.
Hargrave, B. T., 1971. An energy budget for a deposit-feeding amphipod.Limnol. Oceanogr. 16(1): 99–103.
Heiman, D. R., Knight, A. W.. 1975. The influence of temperature on the bioenergetics of the carnivorous stonefly numph,Acroneuria Californica Banks (Plecoptera: Perlidae).Ecology 56: 105–116.
Hunter, R. D., 1975. Growth, fecundity, and bioenergetics in three populations ofLymnaea palustris in upstate New York.Ecology 56: 56–63.
Kuenzler, E. J., 1961. Structure and energy flow of a mussel population in a Georgia salt marsh.Limnol. Oceanogr. 6: 191–204.
Li Zhisheng, Liang Xiaoming, Chen Xüdong et al., 1995. Physical and chemical characteristics of lake water in Donghu Lake.In: Liu Jiankang ed., Ecological Study of Donghu Lake (II), the Scientific Press, Beijing, p. 36–74. (in Chinese)
Marchant, R., 1978. The energy balance of the Australian brine shrimpParartemia zietziana (Crustacea: Anostraca).Freshwat. Biol. 8: 481–489.
Mattice, F. S., 1970. Trophic biology of a natural population ofBithynia tentaculata (L.) in terms of ecological energetics. Ph. D. Dissertation. Syracuse Univ. Syracuse. 122p.
McMahon, R. F., 1972. Interpopulation variation and respiratory acclimation in the bioenergetics of Laevapex fuscus. Ph. D. Dissertation. Syracuse University., Syracuse. 163 p.
Odum, H. T., 1957. Trophic structure and productivity of Silver Springs, Florida.Ecol. Monogr. 27: 55–112.
Odum, E. P., Smalley, A. E., 1959. Comparison of population energy flow of a herbivorous and a deposit-feeding invertebrate in a salt marsh ecosystem.Pro. Natl. Acad. Sci. 45(4): 617–622.
Paine, R. T., 1965. Natural history, limiting factors and energetics of the opisthobranchNavanax inermis.Ecology 46: 603–619.
Paine, R. T., 1971. Energy flow in a natural population of herbivorous gastropod.Tegula funebralis.Limnol. Oceanogr. 16(1): 86–98.
Riisgard, H. U., Randlov, A., 1981. Energy budgets, growth and filtration rate inMytilus edulis at different algal concentrations.Mar. Biol. 61: 227–234.
Teal, J. M., 1962. Energy flow in the salt marsh ecosystem of Georgia.Ecology 43: 614–624.
Tilly, L. J., 1968. The structure and dynamics of Cone spring.Ecol. Monogr. 38: 169–197.
Yan Yunjun, Liang Yanling, Wang Hongzhu, 2000. Annual production ofBellamya aeruginosa in Houhu Lake.J. Lake Sci. 12(1): 68–72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project No. 3960019 and 39430101 supported by NSFC and also a granted for the East Lake Ecological Experimental Station, CAS, Wuhan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yun-jun, Y., Yan-ling, L. & Hong-zhu, W. Energy flow ofBellamya aeruginosa in a shallow algal lake, Houhu Lake (Wuhan, China). Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 19, 243–248 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02850661
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02850661