Abstract
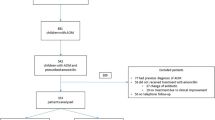
Ciprofloxacin 0.3%/dexamethasone 0.1% (CIP/DEX) and neomycin 0.35%/polymyxin B 10,000 IU/mL/hydrocortisone 1.0% (NPH) were compared for relief of pain in patients with acute otitis externa. Patients received 7 d of treatment with CIP/DEX twice daily or NPH 3 times daily. Ear pain was assessed by patients/caregivers twice daily and by the study investigator on days 3, 8, and 18 (4-point scale). Higher percentages of CIP/DEX-treated patients had relief of severe pain over time (P=.0013) and relief of significant pain (moderate or severe pain) over time (P=.0456), compared with NPH-treated patients. The percentage of CIP/DEX-treated patients with severe pain decreased rapidly within the first 12 h; this contrasted with an increase in pain among NPH-treated patients. CIP/DEX-treated patients had significantly less inflammation (P=.0043) and edema (P=.0148) than NPH-treated patients. Overall, these results support greater pain relief attained over the first 3 d in patients with acute otitis externa treated with CIP/DEX compared with NPH and a rapid reduction in severe pain after initiation of treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosenfeld RM, Brown L, Cannon CR, et al. Clinical practice guideline: acute otitis externa.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006; 134: S4-S23.
Hirsch BE. Diseases of the external ear. In: Bluestone CD, Stool SE, Kenna MA, eds.Pediatric Otolaryngology, vol 1, 3rd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1996: 379–381.
Stroman DW, Roland PS, Dohar J, Burt W. Microbiology of normal external auditory canal.Laryngoscope. 2001; 111: 2054–2059.
Roland PS, Stroman DW. Microbiology of acute otitis externa.Laryngoscope. 2002; 112: 1166–1177.
Marcy M. Swimmer’s ear: timely management tips.Patient Care. 1987; 21: 28–31.
Schwartz RH. Once-daily ofloxacin otic solution versus neomycin/polymyxin B sulfate/ hydrocortisone otic suspension four times a day: a multicenter, randomized, evaluator-blinded trial to compare the efficacy, safety, and pain relief in pediatric patients with otitis externa.Curr Med Res Opin. 2006; 22: 1725–1736.
Meikle AW, Tyler FH. Potency and duration of action of glucocorticoids: effects of hydrocortisone, prednisone and dexamethasone on human pituitary-adrenal function.Am J Med. 1977; 63: 200–207.
Cantrill HL, Waltman SR, Palmberg PF, Zink HA, Becker B.In vitro determination of relative corticosteroid potency.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975; 40: 1073–1077.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roland, P.S., Younis, R. & Wall, G.M. A comparison of ciprofloxacin/dexamethasone with neomycin/polymyxin/ hydrocortisone for otitis externa pain. Adv Therapy 24, 671–675 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02848792
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02848792