Abstract
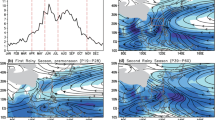
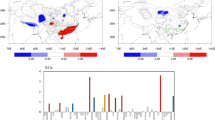
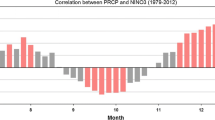
Relationship between the onset data of South China Sea (SCS) summer monsoon and the summer rainfall in Shandong Province was examined by comprehensive analysis to establish a conceptual model of the link. If the summer monsoon occurs earlier, the 500 hPa level would induce the teleconnection of Eurasian pattern in the summer (June–August), which indicates that the western Pacific subtropical high is displaced northward further than usual, the Siberian high is intensified and the Okhotsk low is deepened. Under such circumstance, Shandong, Iocated in the west side of the subtropical high and in front of the mid-Siberia high, would be expected to have a wet summer because it is quite possible for cold and warm air to meet and interact with each other in Shandong. Statistical analysis revealed that the 500 hPa anomalies over Korea and Japan were sensitive to the SCS monsoon onset date and very important to precipitation in Shandong, and that the convective activities over the deep water basin in the SCS in 24–26 pentads significantly influenced the position of the ridge line of the western Pacific subtropical high. These findings yielded better understanding of the causative mechanisms involved in the precipitation generation, so that the knowledge gained can possibly be applied for long-lead forecast.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
He, J. H., Y. H. Ding, H. Gao et al., 2001. Identification of the onset of the SCS monsoon and its indices. China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 123p. (in Chinese)
He, Y., C. M. Peng, C. H. Wu et al., 2000. Interannual variations of the onset of the South China Sea summer monsoon and low-frequency oscillation of convective activities in the atmosphere.Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Science 24(6): 785–793. (in Chinese)
Li, C. Y. and L. P. Zhang, 1999. Summer monsoon activities in the South China Sea and its impacts.Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 23(3): 257–266. (in Chinese)
Liu, Q. Y., P. H. Liu, Y. L. Jia et al., 2001. An index to determine the onset data of the SCS summer monsoon.In: He J. H. et al. eds, Identification of the onset of the SCS monsoon and its indices. China Meteorological Press, Beijing, p. 71–76. (in Chinese)
National Climate Center of China, 1998. 98′ severe floods of China and the climatic anomalies. Meteorological Press, Beijing, 139p. (in Chinese)
Tao, S. Y. and L. X. Chen, 1987. A review of recent research on the East Asian summer monsoon in China.In: Monsoon Meteorology, Oxford University Press. p. 60–92.
Tao, S. Y., W. M. Zhu and W. Zhao, 1988. On the interannual variations of mei-yu. ScientiaAtmospherica Sinica (Special issue): 13–21. (in Chinese)
Xie, A., X. Liu and Q. Ye, 1997. Equatorial vortex and the onset of the summer monsoon over South China Sea.Acta Meteorologica Sinica 55(5): 611–619. (in Chinese)
Ye, D. Z., R. H. Huang, S. W. Wang et al., 1996. Study on the Law and Causes of Drought/flood in Changjiang River and Yellow River Valleys, Shandong Scientific and Technological Press, Jinan. 387p. (in Chinese)
Zhang, S. P, P. S. Zhu and G. F. Hu, 1997. Relationship among summer rainfall in Shandong and North Pacific SST and atmospheric circulations.Meteorological Monthly 23(4): 3–8. (in Chinese)
Zhang, S. P., L. P. Li and P. X. Wang, 2000. Relationship between summer rainfall in Shandong province and the regional features of atmosphere-ocean interaction in tropic zones.Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology 23(4): 594–600. (in Chinese)
Zhang, S. P. and S. C. Jiang, 2001. Possible Influences of ITCZ in Asian Monsoon Regions on Rainy Season Anomaly of North China.Advances in Atmospheric Science 18(5): 1018–1028.
Zhang, S. P., Q. Y. Liu, D. L. Gong, et al., 2004. Influence of the convection over the South China Sea on the summer precipitation of Shandong province.Journal of Ocean University of China 3(1): 18–23.
Zhu, Q.G., H. Wu and L. A. Xie, 1987. Break process and the structural characteristics of Asian summer monsoon trough.Journal of Tropical Meteology 3: 1–8. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is sponsored by natural science fund of Shandong, Province (No.Y2003E01)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suping, Z., Qinyu, L. & Jianbo, W. The link between interannual variation of the South China Sea summer monsoon onset and summer precipitation in Shandong Province. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 23, 275–283 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02847149
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02847149