Abstract
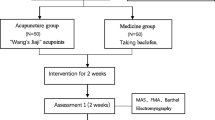
Objective: To investigate the clinical significance of treating post-apoplectic limb spasm by puncturing the acupoints of Governor Vessel as a main therapy. Methods: Twentynine patients with post-apoplectic limb spasm were treated by puncturing the acupoints of Governor Vessel plus the acupoints adjacent to joints, together with another 29 patients treated by conventional acupoints for comparison of the curative effects. Results: Before treatment, there was no significant difference in Ashoworth limb tension score and Fugl-Meyer motor function score between the two groups of patients (P>0.05). After treatment, there was significant difference in tension score between the two groups (P<0.05). Motor function score significantly increased as compared with that before the treatment in both groups (P<0.01), but limb motor function improved more obviously in the treatment group than in the control group (P<0.05). Conclusion: To puncture the acupoints of Governor Vessel as a main therapy can significantly improve the curative effect in the treatment of post-apoplectic limb spasm than conventional acupuncture method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
1995' Fourth National Conference on Cerebrovascular Diseases. Diagnostic Essential Points of Various Cerebrovascular Diseases. China Journal of Neurology, 1996, 29(6): 379.
YUAN Yu, YAN Shang-cheng, CHEN Xiao-hong, et al. Treatment of Spinal Muscular Spasm by Electric Stimulation on Trans-acupoint Skin. China Journal of Medicine, 1993, 73(10): 593.
WANG Xi-quan, ZHANG Jing. Early Stage Rehabilitation of Hemiplegia in Acute Cerebrovascular Diseases. China Journal of Rehabilitative Medicine, 1998, 3(10): 28.
WANG Fu-ping. Promotion of Muscular Tension Restoration in Apoplectic Patients by Acupuncture plus Sports Restudy. China Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation, 2003, 25(12): 28.
WU Yi, AN Hua, SHI Gui-zhen, et al. Clinical Observation on Therapeutic Effects in Apopletic Patients by Routine Rehabilitative Treatment plus Electric Stimulation on Nerves and Muscles. China Journal of Rehabilitative Medicine, 2004, 19(1): 25.
LI Bao-tian. Clinical Study on Treatment of Apoplectic Hemiplegia by Acupuncture on Governor Vessel in Predominance. Shanghai Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, 2002, 21(1): 13.
ZHOU Bing, XIE Mo-dan. Observation of Therapeutic Effect in Treatment of 72 Cases of Apoplectic Aphasia by the Needling Technique to Wake Brain and Open Aperture. Shanghai Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, 2004, 23(1): 9.
Liepert J, Bauder H, Miltner WHR, et al. Treatment-induced Cortical Reorganization After Stroke in Humans. Stroke, 2000, 31: 1210.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Author: ZHANG Wen-dong (1963-), male, junior consultant doctor, a master
Translator: HUANG Guo-qi ({ie29-1})
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen-dong, Z., Xing-sheng, C., Wei, H. et al. Clinical study on treatment of post-apoplectic limb spasm by puncturing acupoints of Governor Vessel. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 3, 26–29 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02845570
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02845570