Abstract
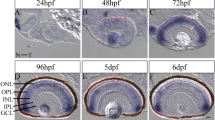
Expression of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in the developing eye of zebrafish was studied by NADPH-diaphorase staining technique. NOS activity was first observed in the optic primordium and the lens placode at 5-somite stage, and remained basically unchanged up to the prim-5 stage. Upon hatching, NOS activity was nearly equally detected in the gangalion cell layer and the photoreceptor layer in the developing retina. However, it began declining in the inner plexiform layer and the inner nuclear layer at this stage. NOS activity disappeared in the lens although the anterior lens epithelium was strongly stained. Two days after hatching, NOS activity was still strong in the photoreceptor layer, but decreased markedly in the gangalion cell layer, the inner plexiform layer and the inner nuclear layer with the retinal patterning. These suggested that nitric oxide (NO), the product of NOS, is not only involved in the modulation of patterning and differentiation of the retinal cells but also in the regulation of proliferation, and differentiation of the lens fibrocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong Hoon Shin and Hyoung Soo Lim, 2000. Immunocytochemical localization of neuronal and inducible nitric oxide synthase in the retina of zebrafish,Brachydanis rerio, Neuroscience Letters 292: 220–222.
Fulvio, F. and G. Vittorio, 2000. Selective nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-diaphorase histochemical labeling of müller radial processes and photoreceptors in the earliest stages of retinal development in the tadpole.Neuroscience Letters 292: 187–190.
Holscher, C., 1997. Nitric oxide, the enigmatic neuronal messenger: its role in synaptic plasticity.Trends Neuroscience 20 (7): 298–303.
Kim, In-Beom, Eun-Jin Lee et al., 1999. Immunocytochemical localization of nitric oxide synthase in the mammalian retina.Neuroscience Letters 267: 193–196.
Lopez-Costa, J. J., J. Goldstein and J. Pecci Saavedra, 1997. Neuronal and macrophagic nitric oxide synthase isoforms distribution in normal rat retina.Neuroscience Letters 232: 155–158.
Luigi, V. and M. Daniela, 2001. The development of NADPH-diaphorase and nitric oxide synthase in the visual system of the cichlid fish,Tilapia mariae.Brain Research Bulletin 54: 569–574.
Luigi, V. and G. Tiziana, 1996. Localization of nitric oxide synthase in the goldfish retina.Brain Research 743: 353–356.
Mitrofanis, J., 1989. Development of NADPH-diaphorase cells in the rat's retina.Neuroscience Letters 102: 165–172.
Palmer, R. M. J., P. S. Ashton and S. Moncada, 1988. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine.Nature (Lond.)333: 664–666.
Ranney Mize, R. and Fu-sun Lo, 2000. Nitric oxide, impulse activity, and neurotrophins in visual system development.Brain Research 886: 15–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The work was supported by Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) of China (G1999012006).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yongjun, W., Shicui, Z. & Sawant, M.S. Expression of nitric oxide synthase in the developing eye of ZebrafishDanio rerio . Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 22, 399–402 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02843635
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02843635