Abstract
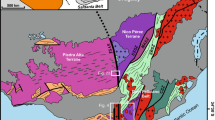
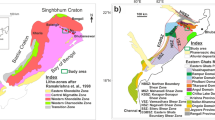
The progressive deformation of the Singhbhum Shear Zone (SSZ) involved the initiation of a mylonitic foliation, its deformation by three generations of reclined folds and superposition of two later groups of folds, i.e., a group of asymmetric folds with subhorizontal or gently plunging axes and a group of gentle and open, transverse and more or less upright folds. The occurrence of sheath folds and U-shaped deformed lineations indicate that the reclined folds were produced by rotation of fold hinges through large angles. The total displacement along the SSZ was compounded of displacements along numerous mesoscopic shear zones. The cleavages in the shear lenses and the mesoscopic shear zones cannot be distinguished as C and S surfaces. They have the same kinematic significance and were produced by ductile deformation, although there were localized discontinuous displacements along both sets,-of cleavages. A mylonitic foliation had formed before the development of the earliest recognizable folds. Its time of formation and folding could be synchronous, diachronous or partly overlapping in time in the different domains of the SSZ.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berthe D, Choukroune P and Jegouzo P 1979 Orthogneiss, mylonite and non-coaxial deformation of granites: The example of South Armorican Shear Zone;J. Struct. Geol. 1 31–42
Coward M P and Kim J N 1981 Strain within thrust sheets; In:Thrust and Nappe Tectonics (ed) K McClay and N J PriceSpec. Publ. Geol. Soc. London 275–292
Dunn J A and Dey A K 1942 The geology and petrology of eastern Singhbhum and the surrounding areas;Mem. Geol. Surv. India 69 281–452
Ghosh S K and Chatterjee A 1985 Patterns of deformed early lineations over late folds formed by buckling and flattening;J. Struct. Geol. 7 651–666
Ghosh S K and Sengupta S 1984 Successive development of plane noncylindrical folds in a progressive deformation;J. Struct. Geol. 6 703–709
Ghosh S K and Sengupta S 1987a Progressive evolution of structures in a ductile shear zone;J. Struct. Geol. 9 277–288
Ghosh S K and Sengupta S 1987b Structural history of the Singbhum Shear Zone in relation to the northern belt; InGeological Evolution of Peninsular India: Petrological and Structural aspects (ed) A K Saha (Delhi: Hindustan Publishing Corporation) pp 31–44
Ghosh S K and Sengupta S 1990 Singhbhum Shear Zone: Structural transition and a kinematic model;Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet. Sci.)99 229–247
Hobbs B E, Means W D and Williams P F 1976An outline of structural geology (John Wiley & Sons) 571 pp
Jacobson C E1983 Structural geology of Pelona Schist and Vincent thrust, San Gabriel Mountains, California;Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 94 753–767
Meneilly A W and Storey B C 1986 Ductile thrusting within subduction complex on Signy Island, South Orkney Islands;J. Struct. Geol. 8 457–472
Mukhopadhyay D and Deb G K 1995 Structural and textural development in Singhum shear zone, eastern India;Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet. Sci.) 104 385–405
Mukhopadhyay D, Ghosh A K and Bhattacharya S 1975 A reassesment of the structures of the Singhbhum shear zone;Bull. Geol. Min. Metall. Soc. India 48 49–67
Naha K 1954 On the continuation of Singhbhum shear belt into Mayurbhanj;Sci. and Cult. 20 295–297
Naha K 1955 A preliminary note on the geometry of folds around Galudih and Ghatsila, Singhbhum, Bihar;Sci. Cult. 20 614–615
Naha K 1956 Structural set-up and movement plan in parts of Dhalbhum, Bihar;Sci. Cult. 22 43–45
Naha K 1965 Metamorphism in relation to stratigraphy, structure and movements in parts of East Singhbhum, eastern India;Q. J. Geol. Min. Metall. Soc. India 37 41–88
Roberts J L 1974 The structure of the Dalradian rocks in the SW highlands of Scotland;J. Geol. Soc. London 130 93–124
Roy A B 1969 The kinematic significance of small structures from a part of the Singhbhum thrust belt;Proc. Natl. Inst. Sci. India A35 103–117
Sarkar S N and Saha A K 1962 A revision of the Precambrian stratigraphy and tectonics of Singhbhum and adjacent regions;Q. J. Geol. Min. Metall. Soc. India 34 97–136
Sarkar S N and Saha A K 1977 The present status of Precambrian stratigraphy, tectonics and geochronology of Singhbhum-Keonjhar-Mayurbhanj region, eastern India;Indian J. Earth. Sci. 37–65
Sengupta S 1977 Deformation of pebbles in relation to associated structures in parts of singhbhum Shear Zone, eastern India;Geol. Rundsch. 66 175–192
Turner F J and Weiss L E 1963Structural analysis of metamorphic tectonites (McGraw-Hill) 545 pp
Williams P F 1985 Multiply deformed terranes-problems of correlations;J. Struct. Geol. 7 269–280
Williams G. D. and Chapman T J 1979 The geometrical classification of non-cylindrical folds;J. Struct. Geol. 1 181–185
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sengupta, S., Ghosh, S.K. The kinematic history of the Singhbhum Shear Zone. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet Sci.) 106, 185–196 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02843446
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02843446