Abstract
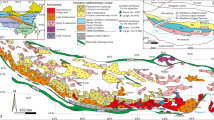
There are two main types of iron deposits in the Middle-Lower Yangtze Valley district. Both of them underwent post-magmatic hydrothermal processes during ore formation. Iron in the hydrothermal ore bodies was derived largely through mobilization from substantially consolidated dioritic intrusives.
Wall-rock alteration zonation indicates that iron-mobilizing hydrothermal fluids evolved in a trend of decreasing alkalinity, which is suggested by regularly distributed wall-rock alterations formed by iron-mobilizing hydrothermal fluids and is in contradiction with the current chloride, chloride complex and bicarbonate models for iron mobilization. The close association of carbonatization with iron ores and the high concentrations of reduced gases such as CO, CH4 and H2 in fluid inclusions suggest that iron is most probably transported in the form of iron carbonyls during post-magmatic hydrothermal processes.
In the light of the iron carbonyl mobilization model, explanations are made of the constraints on ores of some geological factors such as melanocratic alteration, carbonatization, carbonate strata, structural fractures, cryptoexplosive pipes and embryo ores.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson, A.W., 1973, A Text Book of Physical Chemistry: New York, Academic Press, 1709p.
Andlieva, T. A., A. N. Wasilieyeva, B. E. Molchanov, and A. I: Pavlov, 1977, Fluid inclusion compositions in iron ore minerals from Siberia and some problems related to metallogenesis, in Magmatism and Material Problems during Metallogenesis: Siberia Science Press, p.71–93.
Boctor, N.Z., R. K. Popp, and J. D. Frantz, 1980, Mineral-solution equilibria-IV. Solubilities and thermodynamic behaviour of FeCl2 in the system of Fe2O3-H2-H2O-HCl: Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v. 44, p. 1509–1518.
Cao Ronglong, Zhao Bin, Zeng Yishan and Ai Ruiyin, 1980, Experiments on petrogenesis and ore genesis: Beijing, Geological Publishing House, 304p. (in Chinese)
Crerar, D.A., S. A. Wood, and S. L. Brantley, 1985, Chemical control on solubility of ore-forming minerals in hydrothermal solutions: Canadian Mineral., v. 23, p. 333–352.
Du Letian, 1992, The silica bridge problem with special reference to concept changes in hydrothermal metallogeny: Mineral Deposits, v. 11, p. 11–20 (in Chinese with an English abstract).
Ellis, A.J., 1959, The solubility of calcite in carbon dioxide solutions: Am. J. Sci., v. 257, p. 354–365.
Fu Xiancai and Chen Ruihua, 1979, Physical Chemistry, Revised edition: Beijing, People’s Education Publishing House, 534p. (in Chinese)
Ganeyev, I.G., 1984, A physico-chemical model for the transport of mineral material by hydrothermal solutions: Intl. Geol. Rev., v. 27, p. 129–140.
Geology Department of Nanjing University, 1979, Geochemistry, Revised edition: Beijing, Science Press, 507p. (in Chinese).
Gu Lianxing, 1981, Genesis of the mid-Triassic strata-bound iron deposits in the Lower Yangtze River Belt: Thesis for Master degree, Department of Geology, Nanjing University, 93p. (in Chinese).
Gu Lianxing and Ruan Huichu, 1988a, On the hydrothermal origin of the Gushan iron ore deposits in Anhui Province: Mineral Deposits, v. 7, p. 21–28 (in Chinese with an English abstract).
Gu Lianxing and Ruan Huichu, 1988b, Iron carbonyl mobilization model and some constraints on ore genesis, Third National Symposium on Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry: Chongqing Branch of Scientific and Technological Publishing House, p.52–54(in Chinese).
Gu Lianxing and Ruan Huichu, 1990, Constraints on the precipitation of ores from hydrothermal fluids in the two types of iron deposits within the Nanjing-Wuhu area: Mineral Deposits, v. 9, p. 112–118 (in Chinese with an English abstract).
Hieber, V. W., and F. Leutert, 1932a, über metallcarbonyle XII. Die Basenreaktion des eisenpentacarbonyls und die bildung des eisencarbonylwasserstofls: Z. Anorg. U. Allgem. Chem., v. 204, p. 145–164.
Hieber, V.W. and F. Leutert, 1932b, über metallcarbonyle XIII. Der mechanismus der Zersetzungsreaktionen des eisencarbonylwasserstoffs darstellung von eisentetracarbonyl: Z. Anorg. U. Allgem. Chem., v. 204, p. 165–178.
Hoare, D.E. and A.D. Walsh, 1954, The oxidation of carbon monoxide: Trans. Faraday Soc., v. 50 (Part 1), p. 37–50.
Holland, H.D. and S.D. Marlini, 1979, The solubility and occurrence of non-ore minerals, in H. L. Barnes, ed., Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits: 2nd edition, New York, John Wiley & Sons, p. 461–508.
Hsu Kechin, Chu Kingtsu and Ren Chikiang, 1980, On the origin of some iron and copper deposits in several marine fault depressions of southeastern China, in Scientific Papers on Geology for International Exchange, Prepared for the 26th International Geological Congress, Part 3, Metallogenesis and Mineral Ores: Beijing, Geological Publishing House, p. 49–58(in Chinese).
Huheey, J.E., 1978, Inorganic Chemistry: Principle of Structure and Reactivity: Second edition, New York, Harper and Row, 889p.
Hu Shouxi, Sun Mingzhi, Ren Qijiang, Zheng Shujuan and Ye Jun, 1977, Alkaline metasomatism and metallogeny of related intrusions in the Lower Yangtze district: J. Nanjing University, n. 2, p. 91–112 (in Chinese).
Hu Shouxi et al., 1980, Petrography of Metasomatic Rocks: Beijing, Geological Publishing House, 214p. (in Chinese).
Kirk, R. E. and D. F. Othmer, eds., 1978, Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology: 3rd edition, John Wiley & Sons, v. 4, p.794–814.
Kleinberg, J., ed., 1963, Inorganic Syntheses (Chinese edition): Beijing. Science Press, v.2, p. 211–213 and v.7, p.155–165.
Laudise, R.A., 1970, The Growth of Single Crystals: Englewood Cliffs, Prentice-Hall, 352p.
Li Jiuling, Liu Yushan, Miu Wanping and Qu Guolin, 1979, Experiments on albitization of diorite: Acta Geologica Sinica, v. 53, p. 60–73 (in Chinese with an English abstract).
Liu Xiaoshan and Sun Mingzhi, 1983, Characteristics of explosion breccia pipe and its metallogenetic relations to the iron ore deposits at Jishan, Jiangsu Province: J. Nanjing University (Natural Science Edition), n.4, p.712–730 (in Chinese with an English abstract).
Lu Jialan and Fan Wenling, 1980, Experimental study on albitization and iron mobilization in diorite porphyrite at high temperatures: Geochimica, n.3, p.309–319 (in Chinese with an English abstract).
McCarley, R. E., J. L. Templeton, T. J. Colburn, V. Katovic, and R. J. Hoxmeier, 1976, Some unusual dimeric and cluster species of the Group VI transition metals, in R. B. King, ed., Inorganic Compounds with Unusual Properties: Published by the American Chemical Society, p.318–334.
Mullins, B. P. and S.S. Penner, 1959, Explosions, Denotations, Flammability and Ignition: Pergamon Press, 287p.
Nicholls, D., 1973, Iron, in J. C. Bailar, H. J. Emeleus, S. R. Nyholm, and A. F. T. Dickenson, eds., Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry: Pergamon Press, v.3, p.979–1051.
Nicholls, D., 1974, Complex and First-Row Transition Elements: London, MacMillan, 215p.
Ningwu Research Group, 1978. Porphyrite-related Iron Deposits in the Nanjing-Wuhu District: Beijing, Geological Publishing House, 196p. (in Chinese)
Norton, D. L. and L. M. Cathles, 1973. Breccia pipes—products of exsolved vapour from magma: Econ. Geol., v. 68, p. 540–546.
Ore Genesis Lab (Guiyang Institute of Geochemistry, Academia Sinica), 1978, Experimental study on mineralization conditions of rich iron ores in the Nanjing-Wuhu district, in Collection of research papers on rich iron ores: Beijing, Science and Technology Press. p. 272–281 (in Chinese).
Ruan Huichu, Gu Lianxing, Zheng Sujuan and Ye Jun, 1982, On the origin of the Middle Triassic stratiform and strata-bound iron ore deposits in the Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River: J. Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), n.3, p.754–772 (in Chinese with an English abstract).
Ruan Huichu and Gu Lianxing, 1983, Carbonatization and iron mobilization in the mid-Triassic strata-bound ore deposits of the Lower Yangtze River district: Geology and Prpspecting, n.6, p. 11–18 (in Chinese).
Xie Youchang and Shao Meicheng, 1979, Structural Chemistry: Beijing, People’s Education Publishing House. 224p. (in Chinese)
Xu Guangxian and Wang Xiangyin, 1981, Substance Structures: Beijing. People’s Education Publishing House, 556 p.
Zeng Yishan, Ai Ruiying and Wang Fengzhen, 1989, Solubility of the magnetite + hematite buffer assemblage and iron speciation in sodium chloride solutions at 300 °C and 500 bars: Geochimica et Cosmochimica. v. 53, p. 1875–1882.
Zhang Zengfeng, 1991, General features and genetic mechanism of cryptoexplosive breccias: Geological Science and Technology Information, v. 10, p. 1–5 (in Chinese with an English abstract).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lianxing, G., Huichu, R. Hydrothermal mobilization and enrichment of iron in the iron deposits of the Middle-Lower Yangtze Valley district. Chin. J. of Geochem. 12, 228–238 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02843362
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02843362