Abstract
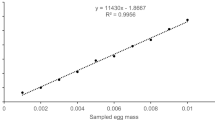
For production enhancement and procedure upgrade, the developmental phases of laboratory-reared eggs of catfishPelteobagrus fulvidraco were investigated. Twenty mature females and 10 males were collected from Dadongmen wholesale fisheries market in Wuhan City on May 8, 2003. Zygotes were stripped from mature fish after hormone-induced ovulation, fertilized, and incubated through whole embryonic development. The fertilized eggs were stocked in density of 100 eggs/L in white square tanks of 10 L. Incubation water was dechlorinated tap water with continuous aeration. The tanks were lit directly with 60 W fluorescent bulbs with a 12 light: 12 dark photoperiod. Water temperature, dissolved oxygen and pH were 29.0±0.5°C, 6.7±0.4 mg/L and 7.4±2, respectively. The results showed that the eggs ofP. fulvidraco were yellow, sticky and contained much yolk. The mean diameter of fertilized eggs was 2.03 mm. At the water temperature of 29.0±0.5°C, the ontogenesis spent about 33 h after fertilization. From fertilization to hatching, the embryonic development can be divided into 30–40 phases, which varies in the emphasis and direction of development. The detailed embryonic movement was also described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berg, L. S., 1964. Freshwater Fishes of the U.S.S.R. and Adjacent Countries Vol. 2, 4th edition. Israel Program for Scientific Translations Ltd, Jerusalem.
Bogutskaya, N. G. and A. M. Naseka, 1996. Cyclostomata and Fishes of Khanka Lake Drainage Area (Amur River basin): an Annotated Check-list with Comments on Taxonomy and Zoogeography of the Region. St. Petersburg. p. 89
Breder, C. M. and D. E. Rosen, 1966. Modes of Reproduction in Fishes. T.F.H. Publications, Neptune City, New Jersey. p. 941
Burgess, W. E., 1989. An atlas of freshwater and marine catfishes: a preliminary survey of the Siluriformes. T.F.H. Publications, Nepture City, New Jersey.
Chen, Y. and G. Wei, 1995. Study on embryonic development ofPelteobagrus vachelli.Journal of Southwest Agricultural University 17(5): 414–417 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Du, J. R., 1963. Studies on the reproduction and feeding habit of yellow catfish in Liangzi Lake.Journal of Zoological Research 2: 74–77 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Kottelat, M., 2001a. Fishes of Laos. Wildlife Heritage. Trust Publications, Colombo, p. 198
Kottelat, M., 2001b. Freshwater Fishes of Northern Vietnam. Environmental and Social Development Unit, East Asia and Pacific Region, World Bank, Washington iii. p. 140
Nelson, J. S., 1994. Fishes of the World, 3. John Wiley and Sons, New York, p. 600
Ochi, H., A. Rossiter and Y. Yanagisawa, 2002. Paternal mouthbrooding bagrid catfishes in Lake Tanganyika.Ichthyol. Res. 49: 270–273.
Wang, L. L., Q. R. Chou, S. P. Zou, H. W. Liu, and F. H. Wu, 1989. Observation on embryonic and post-embryonic development of yellow catfish.Freshwater Fisheries 5: 9–12 (in Chinese)
Wang, W. B., C. D. Zhu, X. S. Zhong, S. Z. Chen and Y. L. Zhang, 1980. A study on artificial fertilization and early development ofNeosalanx tangkahkeii taihuensis in autumn.Journal of Chinese Fisheries 4(3): 303–307 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wei, G., 1987. Preliminary study on hybrid betweenPelteobagrus vachelli andLeiocassis longirostris.Freshwater Fisheries 6: 14–17 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wei, G., L. Huang, Y. Chen, L. H. Lu and G. F. Jiang, 2002. Observation on the embryonic development ofPseudobagrus nitidus.Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Natural Science)27(4): 567–571 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xie, X. J., 1986. On embryonic development ofSilurus meridionalis.Journal of Southwest Normal University (Natural Science Edition)3(2): 72–78 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang, K. X., 1998. On the embryonic development of Salangichthys (Neosalanx) tangkahkeii taihuensis.Journal of Lake Science 10(1): 55–61 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang, Y., 1987. A taxonomic study on the Chinese icefishes of genus Neosalanx (Pisces: Salangidae) with description of a new species from the Taihu Lake.Zoological Research 8: 272–286 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang, Y. G., D. S. Wang and Q. S. Luo, 1996. An observation on the embryonic development ofMystus macropterus (Bleeker).Journal of Southwest Normal University (Natural Science Edition)16(2): 223–224 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu, Z. Y., 1982. On embryonic development ofClarias fuscus.Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica 7(4): 445–453 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Scientific and Technological Bureau of Wuhan City, Hubei Province (No: 20012009105-4)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weimin, W., ABBAS, K. & Ansheng, Y. Embryonic development ofPelteobagrus fulvidraco (Richardson, 1846). Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 24, 378–383 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842853
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842853