Abstract
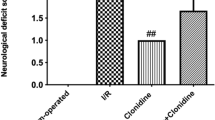
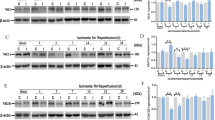
Objective: To determine the protective effect of monosialoganglionside (GM1) and evaluate the influence of GMI on expression of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 1 (NMDAR1) in Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats with focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R). Methods: Left middle cerebral artery (MCA) was occluded by an intraluminal suture for 1 h and the brain was reperfused for 72 h in SD rats when infarct volume was measured. GM1 (10 mg/kg) was givenip (intraperitoneally) at 5 min (group A), 1 h (group B) and 2h (group C) after MCA occlusion (MCAo). Expression of NMDAR1 was detected by Western blot at various time after reperfusion (4 h, 6 h, 24 h, 48 h and 72 h) in ischemic hemispheres of the rats with or without GM1 administered. Results: (1) Adjusted relative infarct volumes of groups A and B were significantly smaller than that of group C and the control group (P<0.01, andP<0.05, respectively). (2) Expression level of NMDAR1 was temporally high at 6 h after reperfusion, and dipped below the normal level at 72 h after reperfusion. GM1 at 5 min after MCAo significantly suppressed the expression of NMDAR1 at 6 h after reperfusion (P<0.05 vs the control). At 72 h after reperfusion, the NMDAR1 expression level of rats treated with GM1 administered (at 5 min or 2 h after MCAo) was significantly higher than that of the control (P<0.05). Conclusion: GM1 can time-dependently reduce infarct volume in rats with focal cerebral I/R partly through stabilizing the expression of NMDAR1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brandoli, C., Sanna, A., De Bernardi, M.A., Follesa, P., Brooker, G., Mocchetti, I., 1998. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and basic fibroblast growth factor down-regulate NMDA receptor function in cerebellar granule cells.J Neurosci,18(19):7953–7961.
Choi, D.W., Rothman, S.M., 1990. The role of glutamate neurotoxicity in hypoxic-ischemic neuronal death.Annu Rev Neurosci,13:171–182.
Collingridge, G.L., Singer, W., 1990. Excitatory amino acid receptors and synaptic plasticity.Trends Pharmacol Sci,11(7):290–296.
de Erausquin, G.A., Manev, H., Guidotti, A., Costa, E., Brooker, G., 1990. Gangliosides normalize distorted single-cell intracellular free Ca2+ dynamics after toxic doses of glutamate in cerebellar granule cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,87(20):8017–8021.
Duchemin, A.M., Ren, Q., Mo, L., Neff, N.H., Hadjiconstantinou, M., 2002. GM1 ganglioside induces phosphorylation and activation of Trk and Erk in brain.J Neurochem,81(4):696–707.
Friedman, L.K., Ginsberg, M.D., Belayev, L., Busto, R., Alonso, O.F., Lin, B., Globus, M.Y., 2001. Intraischemic but not postischemic hypothermia prevents non-selective hippocampal downregulation of AMPA and NMDA receptor gene expression after global ischemia.Brain Res Mol Brain Res,86(1–2):34–47.
Garofalo, L., Cuello, A.C., 1994. Nerve growth factor and the monosialoganglioside GM1: analogous and different in vivo effects on biochemical, morphological, and behavioral parameters of adult cortically lesioned rats.Exp Neurol,125(2):195–217.
Kang, T.C., Hwang, I.K., Park, S.K., An, S.J., Yoon, D.K., Moon, S.M., Lee, Y.B., Sohn, H.S., Cho, S.S., Won, M.H., 2001. Chronological changes ofN-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and excitatory amino acid carrier 1 immunore-activities in CA1 area and subiculum after transient forebrain ischemia.J Neurocytol,30(12):945–955.
Kharlamov, A., Guidotti, A., Costa, E., Hayes, R., Armstrong, D., 1993. Semisynthetic sphingolipids prevent protein kinase C translocation and neuronal damage in the perifocal area following a photochemically induced thrombotic brain cortical lesion.J Neurosci,13(6):2483–2494.
Longa, E.Z., Weinstein, P.R., Carlson, S., Cummins, R., 1989. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats.Stroke,20(1):84–91.
Luo, J., Bosy, T.Z., Wang, Y., Yasuda, R.P., Wolfe, B.B., 1996. Onlogeny of NMDAR1 subunit protein expression in five regions of rat brain.Brain Res Dev Brain Res,92(1):10–17.
Luo, J., Wang, Y., Yasuda, R.P., Dunah, A.W., Wolfe, B.B., 1997. The majority of n-methyl-d-aspartate receptor Complexes in adult rat cerebral cortex contain at least three different subunits (NMDAR1/NMDAR2A/NMDAR2B).Mol Pharmacol,51(1):79–86.
Manev, H., Favaron, M., Vicini, S., Guidotti, A., Costa, E., 1990. Glutamate-induced neuronal death in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells: protection by synthetic derivatives of endogenous sphingolipids.J Pharmacol Exp Ther,252(1):419–427.
Michaels, R.L., Rothman, S.M., 1990. Glutamate neurotoxicity in vitro: antagonist pharmacology and intracellular calcium concentrations.J Neurosci,10(1):283–292.
Monaghan, D.T., Bridges, R.J., Cotman, C.W., 1989. The excitatory amino acid receptors: their classes, pharmacology, and distinct properties in the function of the central nervous system.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol,29:365–402.
Rossi, D.J., Oshima, T., Attwell, D., 2000. Glutamate release in severe brain ischemia is mainly by reversed uptake.Nature,403(6767):316–321.
Simon, R.P., Chen, J., Graham, S.H., 1993. GM1 ganglioside treatment of focal ischemia: a dose-response and microdialysis study.J Pharmacol Exp Ther,265(1):24–29.
Wahlestedt, C., Golanov, E., Yamamoto, S., Yee, F., Ericson, H., Yoo, H., Inturrisi, C.E., Reis, D.J., 1993. Antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to NMDA-R1 receptor channel protect cortical neurons from excitotoxicity and reduce focal ischaemic infarctions.Nature,363(6426):260–263.
Won, M.H., Kang, T., Park, S., Jeon, G., Kim, Y., Seo, J.H., Choi, E., Chung, M., Cho, S.S., 2001. The alterations ofN-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor expressions and oxidative DNA damage in the CA1 area at the early time after ischemia-reperfusion insult.Neurosci Lett,301(2): 139–142.
Zang, L.H., Wei, E.Q., 2003. Neuroprotective effect of ONO-1078, a leukotriene receptor antagonist, on transient global cerebral ischemia in rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin,24(12):1241–1247.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project (No. 2004QN012) supported by the Youth Talent Special Fund of Health Bureau of Zhejiang Province, the National Basic Research Program (973) of China (No. G1999054000) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30371637)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jian-ren, L., Mei-ping, D., Er-qing, W. et al. GM1 stabilizes expression of NMDA receptor subunit 1 in the ischemic hemisphere of MCAo/reperfusion rat. J Zheijang Univ Sci B 6, 254–258 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842461
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842461