Abstract
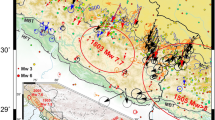
We report the results of the South Indian Strain Measuring Experiment (SISME) designed to determine whether strain related to microseismicity in the past century may have deformed the networks of the 19th century Great Trigonometrical Survey of India (GTS). More than a dozen GTS points were measured between Mangalore, Madras, and Kanyakumari in southernmost India using GPS geodesy to determine regional deformation. Detailed measurements were made near two of the original baselines of the survey to determine the reliability of dilatational strain data for the network. The regional measurements revealed negligible regional dilatational (+ 11.2 + 10 microstrain) and shear strain changes (0.66± 1.2μradians) in the southernmost 530 km of India. In addition to these measurements, we determined the rate of northward and eastward motion of a point in Bangalore (1991–1994) in the ITRF92 reference frame to be 39 ± 3.5 mm/year, and 51 ± 11 mm/year respectively. This is consistent with NUVEL-1A plate motion estimate for India. Simultaneous measurements to a point near Kathmandu reveal that the Indian plate and the Southern Himalaya are moving approximately in unison, placing an upper limit on the rate of creep processes beneath the lesser Himalaya of ≈6 mm/year, and suggesting relatively rigid behavior of the Indian plate north of Bangalore. The stability of the Indian plate is confirmed by the absence of significant changes in the lengths of the two baselines at Bangalore and Cape Comorin, which, within the limits of experimental error have not changed since 1869. The measurements place an upper limit for recent deformation in the southern peninsula, and hence a lower limit for the renewal time for intraplate earthquakes in the region of approximately 10,000 years, assuming shear failure strain of approximately 100 μradians. This, in turn, implies that recurrence intervals for Peninsular Earthquakes far exceed the length of the written historic record, suggesting that the characterisation of seismic recurrence intervals from historical studies is likely to be fruitless. In contrast, the SISME experiment demonstrates that the noise level of geodetic studies based on 19th century GTS data is less than 0.02 μstrain/year, providing considerable scope for delineating regions of anomalously high seismogenic strain, by GPS measurements at all available trig points of the 19th century GTS survey.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blewitt G M, Heflin W, Bertiger F, Webb U, Lindquister, Malla R 1992 Global coordinates with centimetre accuracy in the International Terrestrial Reference Frame using Global Positioning System;GRL 19 853–56
Bürgmann R and 5 authors 1994 Intraplate deformation and interplate convergence in India: Bangalore/ Kathmandu baseline changes 1991–1994;Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. 75 184–185
Bomford G 1971Geodesy, 3rd edition, (Oxford University Press) 731 pp.
Clarke A R 1866Comparisons of the Standards of Length of England, France, etc., (London)
De Mets Charles, Gordon Richard and Vogt Peter 1994 Location of the Africa-Australia-India-triple junction and motion between the Australian and Indian plates: Results from an aeromagnetic investigation of the central Indian and Carlsberg ridges;Geophys. J. Int. 119 893–930
Drew A R and Snay R A 1989 DYNAP: Software for estimating crustal deformation from geodetic data;Tectonophysics 162 331–343
Gaur V K and 7 authors 1994 130 years of seismogeodetic deformation in southern India;Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. 75 185
Gaur V K 1994 Evaluation of seismic hazard in India towards minimizing earthquake risk;Curr. Sci. 67 324–335
Gowd T N, Srirama Rao S V and Gaur V K 1992 Tectonic Stress Field in the Indian Subcontinent;J. Geophys. Res.,97 11879–11888
Jackson M and Bilham R 1994 Constraints on Himalayan Deformation inferred from Vertical Velocity Fields in Nepal and Tibet;J. Geophys. Res.,99 13897–13912
Pavlis N K and Rapp R H 1990 The development of an isostatic gravitational model to degree 360 and its use in global gravity modeling;Geophys. J. Int. 369–378
Rai S S, Ramesh D S, Srinagesh D, Suryaprakasam K, Mohan G, Rajagopala Sarma P V S S, Satyanarayana Y and Gaur V K 1992 Seismic Tomography of the Indian Shield;Curr. Sci. 62 213–226
Rajal B S, Srivastava V P and Madhwal H B, September 1994 GPS brings Unity to Indian Diversity;GPS World 56–60
Rapp R H, Wang Yan Ming, Pavlis N K, August 1991 The Ohio State 1991 Geopotential and Sea Surface Topography Harmonic Coefficient Models;Report No. 410, Department of Geodetic Science and Surveying, Ohio State University, Columbus Ohio 43210–1247
Strahan G 1890 Account of the Operations of the Great Trigonometrical Survey of India. Volume XII. General Description of the Principal Triangulation of the Southern Trigon, including the simultaneous reduction and the details of two of the component series, the Great Arc Meridional-Section 8° to 18°, and the Bombay Longitudinal, Dehra Dun
Walker J T 1870 Account of the Operations of the Great Trigonometrical Survey of India. Volume I. The standards of measure and the baselines, also an Introductory account of the Early operations of the Survey, during the period of 1800–1830, Dehra Dun
Walker J T 1879 Account of the Operations of the Great Trigonometrical Survey of India. Volume II. History and General Description of the Principal Triangulation and of its reduction, Dehra Dun
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, J., Blume, F., Jade, S. et al. Microstrain stability of Peninsular India 1864–1994. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet Sci.) 104, 131–146 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842279
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842279