Abstract
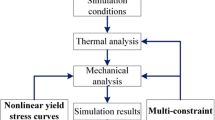
In order to understand the change regulation of residual stress during multi-repaired welding to provide theoretical guidance for correct repaired welding procedure and improvement of joint properties, and to simulate the magnitude and distribution of residual stress using the finite element method (FEM). A model of temperature field of weld-repaired using FEM, which was simplified, was established. The weld stress consists of thermal stress and organization stress. Models of the thermal stress and organization stress were described. ANSYS, a software of finite element, was applied to calculate the stress, BHW35 steel was taken as an example, the simulated and experimental results for the 1st, 3rd and 5th weld-repaired were analyzed, the simulated results are in good agreement with experimental results. It can be concluded that the residual stress in the weld center changes little, and the high residual stress exists in HAZ. And in the same place, the more repaired weld, the higher residual stress, and the area of residual stress becomes wider.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou Zeng-da, Wang Xin-hong, Qu Shi-rao. Numerical Simulation of Residual Stress Eliminated by Hammer in Weld Joint.Chinese Mechanical Engineering, 1999,10(4):466–468
Wang Xin-hong, Qu Shi-rao, Zhou Zeng-da. Numerical Simulation about Stress Field of Repaired Weld for Hard Casting.College Journal of ShangDong Industry University, 1998,28(4):301–306
Chen chu.Application of Numerical Analysis in Welding. Shanghai: Publishing House of ShangHai Transportation University, 1985
Pan Mu, Cheng Yibing, Mary S J Gani. Stress Analysis of Alumina Coatings on Silicon Carbide Baesd Refractories during Thermal Cycling.Journal of Wuhan University of Technology— Mater. Sci. Ed., 1999,14(3):9–15
Li DongLin, Yu YouSheng, Wen JiaLing,et al. 3D Dynamic Simulation Temperature Field of Surfacing.Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Transportation Science& Engineering), 2002, 26(5): 671–673
Tso-Liang, TengaChin-Ping Fung,et al. Effect of Weld Geometry and Residual Stresses on Fatigue in Butt-welded Joints.International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2002, 79:467–482
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
ZHU Yuan-xiang: Born in 1963
Funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.50334050)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan-xiang, Z., Xue-rong, Z., Xiao-fei, Z. et al. Numerical simulation of multi-repaired weld residual stress. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 19, 99–102 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02841381
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02841381