Abstract
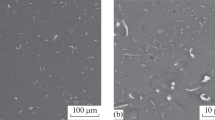
By making castings that pick up gas from moisture in red sand molds, the porosity generated at different cooling rates was discussed during solidification of hypereutectic Al−25% Si alloy without and with phosphorus additions. The effect of phosphorus addition on hydrogen content in the melt was also studied. It was observed that the phosphorus addition made hydrogen content in alloy melts present a “see-saw” tendency. In addition to primary silicon refinement, the phosphorus promoted gas porosity formed not only in slowly cooled sections, but also in rapidly cooled sections. There was a small difference in density of full dense sample between P-refined and unrefined castings, with a larger density associated with phosphorous addition. The change of the surface tension seemed more reasonable to explain the mechanism of porosity behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu L N, Bian X F, Mahto A, Duan Y F. Influence of Elemental Iron on Hydrogen Content in Superheated Aluminum-iron Melts.Journal of Wuhan University of Technology— Materials Science Edition, 2004, 19(2):57–61
Argo D, Gruzleski J E. Porosity in Modified Aluminum Alloy Castings.AFS Transactions, 1984,96:65–74
Jacob S, Fonderie. Investigation on Behavior of Porosity in Srmodified Hypoeutectic Al-Si Alloys.AFS Transcations, 1977,32:13–25
Hu L N, Bian X F, Duan Y F. Influence of Hydrogen Content on the Behavior of Grain Refinement in Hypereutectic Aluminum-silicon Alloy.Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2004,11:141–146
Honer K E. Effect of Ca and Sr on Hydrogen Gas Pickup in Aluminum Melts.Giessereiforschung, 1987,39:34–48
Argo D, Gruzleski J E. Porosity in Modified Aluminum Alloy Castings.AFS Transactions, 1988,96:65–74
Zhang Z H, Bian X F. Refinement and Thermal Analysis of Hypereutectic Al-Si Alloy.Transactions of Nonferrous Metal Society of China, 2001,11(3):374
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
HU Li-na: Born in 1972
Funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.50071028) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No.Z2001F02)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li-na, H., Xiu-fang, B. & You-feng, D. Hydrogen content and porosity behavior of hypereutectic aluminum-silicon alloy with phosphorus. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 19, 65–68 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02841372
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02841372