Abstract
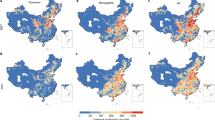
With economic development and living standard improvement, livestock and poultry production has grown up rapidly, also has become the leading source of pollution in vast rural areas in China. The estimated annual loss amount of COD, BOD, NH3-N from manure in 2001 is 7. 28 million ton, 4.99 million ton and 1.32 million ton, respectively. The COD loss amount from manure is close to the sum of COD from industrial and domestic wastewater. Because animal waste and wastewater can enter water bodies from spills or breaks of waste storage structures (due to accidents or excessive rain), and non-agricultural application of manure to cropland, this contamination has resulted in quality degradation of surface and underground drinking water supplies. Areas with concentrated livestock operations are showing elevated nutrients and organic pollutant contents in surface waters. This widespread contamination of water has prompted governments at various levels to adopt regulations and measures to control the spreading of livestock pollution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ding Jianhua (2000) The pollution of poultry and animal feces and the countermeasures in Guangzhou [J].Research of Environmental Sciences.13, 57–59 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Doug Parker (2000) Controlling agricultural nonpoint water pollution: costs of implementing the Maryland Water Quality Improvement Act of 1998 [J].Agricultural Economics.24, 23–31.
Edwards D. R. and Daniel T. C. (1994) Quality of runoff from fescue grass plots treated with poultry litter and inorganic fertilizer [J].J. Environ. Qual. 23, 579–584.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) (1997)Livestock and the Environment; Finding a Balance [R]. pp. 115. Cees de Haan, Henning Steinfeld, Harvey Blackburn, http:// www.fao.org/WAICENT/FAOINFO/AGRICULT/aga/lspa/LXE-HTML/tech
Hooda P. S., Edwards U. A. C., Anderson H. A., and Miller A. (2000) A review of water quality concerns in livestock farming areas [J].The Science of the Total Environment.250, 143–167.
Liu Peifang, Chen Zhenlou, Xu Shiyuan, and Liu Jie (2001) Waste loading and treatment strategies on the excreta of domestic animals in the Yangtze Delta [J].Resource and Environment of Yangtze River Watershed.11, 456–460 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Neeteson J. J. (2000) Nitrogen and phosphorus management on Dutch dairy farms: Legislation and strategies employed to meet the regulations [J].Biol Fertile Soils. 30, 566–572.
Ritter W. F. (2001) Nonpoint source pollution and livestock manure management. InWatershed Management and Hydrology (eds. W. F. Ritter and A. Shirmohammadi) [M]. pp. 136–158. CRC Press LLC, Boca Raton, Florida, USA.
Steinfeld H., De Haan C., and Blackburn H. (1997)Livestock-environment Interactions: Issues and Options [R]. pp. 56. European Commission Directorate-General for Development.
U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (2000)National Management Measures to Control Nonpoint Source Pollution from Agriculture (Draft). (Chapter 4D) [R]. pp. 107–128. Animal Feeding Operations (AFOS).
Wang Xiaoyan, Wang Xiaofeng, Wang Zhengang et al. (2003) Nutrient loss from various land-use areas in Shixia small watershed of Miyun County, Beijing, China [J].Chinese Journal of Geochemistry.22, 173–178.
Wu Yanhong, Wang Sumin, Barttarbee R. W., and Zhu Yuxin (2004) Temporal and spatial distribution of elements in a small catchment, and buffer function of wetland in Longgan Lake, China [J].Chinese Journal of Geochemistry.23, 37–45.
Xu Qian and Zhu Guizheng (2002) Pollution from large-scaled livestock and poultry breeding-farms in Beijing and its control [J].Rural Environmental Science.18, 24–28 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Jinsong, Chen Deming, Liu Guangming, and Li Haifeng (2001) Nutrient cycling and environmental effect of livestock production in case regions of Jiangsu Province [J].China Environmental Science.21, 468–471 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Cungen (1999)Review of the Livestock Revolution in China [R]. Proceeding of the Workshop on the Implication of Asian Economic Crisis for the Livestock Industry. pp. 203–213. Bangkok, Thailand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by the State Ministry of Education and the Beijing Municipal Scientific New-Star Plan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiaoyan, W. Diffuse pollution from livestock production in China. Chin. J. Geochem. 24, 189–193 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02841165
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02841165