Abstract
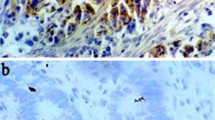
Objectives: To explore the mechanism of development and aggressiveness in gastric carcinomas by investigating the expression and role of CD97 and its cellular ligand CD55 in gastric carcinomas. Methods: Tumor and corresponding normal mucosal tissue, collected from 39 gastric carcinoma patients, were examined by immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR for the expression of CD97 and CD55. Results: CD97stalk was strongly stained on scattered tumor cells or small tumor cell clusters at the invasion front of gastric carcinomas. The expression of CD97stalk was frequently observed in tumors of stage I and T1 gastric carcinoma patients. The expression of CD97stalk between Stage I and Stage II, III, IV specimens showed significant difference (P<0.05), between T1 and T2, T3, T4 specimens also showed significant difference (P<0.05). Specimens with tumor invasion depth limited in mucosa of T1 specimens showed higher positive CD55 expression than specimens with the same tumor invasion depth in T2, T3, T4 specimens, the expression of CD55 between T1 and T2 T3, T4 specimens was significantly different (P<0.05). There was strong correlation between the distribution patterns of CD97stalk and CD55 on tumor tissues (r=0.73,P<0.05). Signet ring cell carcinomas frequently contained strong CD97stalk and CD55-staining. Conclusions: Our results suggest that CD97stalk is probably involved in the growth, invasion and aggressiveness of gastric carcinomas by binding its cellular ligand CD55. CD97stalk and CD55 could be useful as molecular markers for prognosis and therapy of gastric carcinoma patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aust, G., Eichler, W., Laue, S., Lehmann, I., Heldin, N.E., Lotz, O., Scherbaum, W.A., Dralle, H., Hoang-Vu, C., 1997. CD97: A dedifferentiation marker in human thyroid carcinomas.Cancer Res.,57:1798–1806.
Aust, G., Steinert, M., Schutz, A., Boltze, C., Wahlbuhl, M., Hamann, J., Wobus, M., 2002. CD97, but not its closely related EGF-TM7 family member EMR2, is expressed on gastric, pancreatic, and esophageal carcinomas.Am. J. Clin. Pathol.,118(5):699–707.
Boltze, C., Schneider-Stock, R., Aust, G., Mawrin, C., Dralle, H., Roessner, A., Hoang-Vu, C., 2002. CD97, CD95 and Fas-L clearly discriminate between chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in perioperative evaluation of cryocut sections.Pathol Int.,52:83–88.
Brabletz, T., Jung, A., Hermann, K., Gunther, K., Hohenberger, W., Kirchner, T., 1998. Nuclear overexpression of the oncoprotein beta-catenin in colorectal cancer is localized predominantly at the invasion front.Pathol. Res. Pract.,194:701–704.
Brabletz, T., Jung, A., Reu, S., Porzner, M., Hlubek, F., Kunz-Schughart, L.A., Knuechel, R., Kirchner, T., 2001. Variable beta-catenin expression in colorectal cancers indicates tumor progression driven by the tumor environment.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA,98:10356–10361.
Hamann, J., Vogel, B., van Schijndel, G.M., van Lier, R.A., 1996. The seven-span transmembrane receptor CD97 has a cellular ligand (CD55, DAF).J. Exp. Med.,184(3):1185–1189.
Hoang-Vu, C., Bull, K., Schwarz, I., Krause, G., Schmutzler, C., Aust, G., Dralle, H., 1999. Regulation of CD97 protein in thyroid carcinoma.Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.,84:1104–1109.
Jaspars, L.H., Vos, W., Aust, G., van Lier, R.A., Hamann, J., 2001. Tissue distribution of the human CD97 EGF-TM7 receptor.Tissue Antigens,57:325–331.
Kwakkenbos, M.J., Kop, E.N., Stacey, M., Gordon, S., Lin, H.H., Hamann, J., 2004. The human EGF-TM7 family: A postgenomic view.Immunogenetics,55:655–666.
Li, L., Spendlove, I., Morgan, J., Durrant, L.G., 2001. CD55 is over-expressed in the tumour environment.Br. J. Cancer,84(1):80–86.
Maruyama, K., Ochiai, A., Akimoto, S., Nakamura, S., Baba, S., Moriya, Y., Hirohashi, S., 2000. Cytoplasmic beta-catenin accumulation as a predictor of hematogenous metastasis in human colorectal cancer.Oncology,59:302–309.
Mcknight, A.J., Gordon, S., 1998. The EGF-TM7 family: Unsual structures at the leukocyte surface.Leukoc. Biol.,63:271–280.
Mustafa, T., Klonisch, T., Hombach-Klonisch, S., Kehlen, A., Schmutzler, C., Koehrle, J., Gimm, O., Dralle, H., Hoang-Vu, C., 2004. Expression of CD97 and CD55 in human medullary thyroid carcinomas.Int. J. Oncol.,24(2):285–294.
Niehans, G.A., Cherwitz, D.L., Staley, N.A., Knapp, D.J., Dalmasso, A.P., 1996. Human carcinomas variably express the complement inhibitory proteins CD46 (membrane cofactor protein), CD55 (decay-accelerating factor), and CD59 (protectin).Am. J. Pathol.,149(1):129–142.
Nowicki, S., Nowicki, B., Pham, T., Hasan, R., Nagamani, M., 2001. Expression of decay accelerating factor in endometrial adenocarcinoma is inversely related to the stage of tumor.Am. J. Reprod. Immunol.,46(2):144–148.
Remmele, W., Stegner, H.E., 1987. Recommendation for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast cancer tissue.Pathologe,8:138–140.
Shimo, K., Mizuno, M., Nasu, J., Hiraoka, S., Makidono, C., Okazaki, H., Yamamoto, K., Okada, H., Fujita, T., Shiratori, Y., 2004. Complement regulatory proteins in normal human esophagus and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Gastroenterol. Hepatol.,19(6):643–647.
Steinert, M., Wobus, M., Boltze, C., Schutz, A., Wahlbuhl, M., Hamann, J., Aust, G., 2002. Expression and regulation of CD97 in colorectal carcinoma cell lines and tumor tissues.Am. J. Pathol.,161:1657–1667.
Wobus, M., Vogel, B., Schmucking, E., Hamann, J., Aust, G., 2004. N-glycosylation of CD97, within the EGF domains is crucial for epitope accessibility in normal and malignant cells as well as CD55 ligand binding.Int. J. Cancer,112:815–822.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (No. 2004C34010) supported by the Science and Technology Bureau of Zhejiang Province, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yong, L., Li, C., Shu-you, P. et al. Role of CD97stalk and CD55 as molecular markers for prognosis and therapy of gastric carcinoma patients. J. Zheijang Univ.-Sci. B 6, 913–918 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02841003
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02841003