Abstract
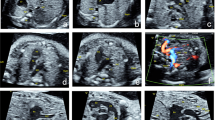
Objective: To study the value of detecting fetal congenital heart disease (CHD) using the five transverse planes technique of fetal echocardiography. Methods: Nine hundred and eighty-two high-risk pregnancies for fetal CHD were included in this study, the fetal heart was scanned with the five transverse planes technique of fetal echocardiography described by Yagel, autopsy was conducted when pregnancy was terminated. Blood from fetal heart was collected for fetal chromosome analysis. A close follow-up was given for normal fetal heart pregnancies and neonatal echocardiography was performed to check the accuracy of prenatal diagnosis. Results: (1) Forty-six cases (4.68%) were found to have fetal heart abnormalities in this study, 69.56% of them were diagnosed by single four-chamber view, another 30.43% fetal CHD were found by combining other views; (2) Forty-one parents of prenatal fetuses with CHD chose to terminate pregnancy, thirty-two of them gave consent to conduct autopsy, 93.75% of which yielded unanimous conclusion between prenatal fetal echocardiography and autopsy; (3) Thirty-two of 46 cases underwent fetal chromosome analysis, 8 cases (25%) were found to have abnormal chromosome; (4) Five cases were found to have right ventricle and atrium a little bigger than those on the left side, with the unequal condition being the same after birth, but there were no clinical manifestations and they are healthy for the time being; (5) Nine hundred and thirty-six cases were not found with abnormality in this study, but one case was diagnosed with ventricular septal defect after birth, one case was diagnosed with patent ductus arteriosus, one case had atrial septal defect after birth. Conclusions: (1) The detected CHD rate was 4.68% by screening fetal heart with five transverse planes according to Yagel's description of high risk population basis for CHD. The coinciding rate of prenatal diagnosis and autopsy was 93.75%; (2) The sensitivity of detecting fetal heart abnormality is 92%, the specificity is 99.6% using the five transverse planes technique of fetal echocardiography; (3) Fetuses with mild or moderate disproportion of right and left side in the heart are potentially healthy babies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan, L.D., 1994. Fetal congenital heart disease: Diagnosis and management.Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol.,6(1): 45–49.
Benacerraf, B.R., Sanders, S.P., 1990. Fetal echocardiography.Radiol. Clin. North. Am.,28(1): 131–147.
Benacerraf, B.R., Pober, B.R., Sanders, S.P., 1987. Accuracy of fetal echocardiography.Radiology,165(3): 847–849.
Ferencz, C., Neill, C.A., Baughman, J.A., Rubin, J.D., Brenner, J.Z., Perry, L.W., 1989. Congenital cardiovascular malformation associated with chromosome abnormalities: An epidemiological study.J. Pediatr.,114(1): 79–86.
Gembruch, U., 1997. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart disease.Prenat. Diagn.,17(13): 1283–1298.
Gillum, R.F., 1994. Epidemiology of congenital heart disease in the United States.Am. Heart. J.,127(4 Pt 1): 919–927.
Hung, J.H., Ng, H.T., Shei, K.S., Pan, Y.P., Yen, K.T., Wang, M.J., Yang, M.L., Shu, L.P., 1991. Using ultrasonic measurement of cardiac size in predicting congenital heart defect.Fetal. Diagn. Ther.,6(1–2): 65–73.
Kleinman, C.S., Nehgme, R.A., 2004. Cardiac arrhythmias in the human fetus.Pediatr. Cardiol.,25(3): 234–251.
Yagel, S., Cohen, S.M., Achiron, R., 2001. Examination of the fetal heart by five short axis views: A proposed screening method for comprehensive cardiac evaluation.Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol.,17(5): 367–369.
Yoo, S.J., Young, H.L., Kyoung, S.C., 1999. Abnormal three-vessel view on sonography: A clue to the diagnosis of congenital heart disease in the fetus.AJR Am. J. Roentgenol.,172(3): 825–830.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Start-up Fund for Study-abroad Returnee, Ministry of Education, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hui, L., Jun, W., Ying, M. et al. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital fetal heart abnormalities and clinical analysis. J. Zheijang Univ.-Sci. B 6, 903–906 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02841001
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02841001