Abstract
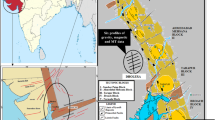
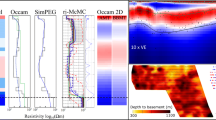
This paper reviews the validity of earlier models obtained after quantitative interpretation of GDS data and presents a fresh model using the inversion scheme EM2INV. The 2-D inversion of data is more objective than the earlier interpretation performed by using trial and error method. The inversion results indicate that the present model differs from the earlier ones. The reason could be that available GDS data are sufficient only for deriving the horizontal variation of subsurface resistivity. In order to study the vertical resistivity variation additional MT sounding data would be required. It would therefore be desirable to carry out MT survey in the specified area. A more comprehensive/appropriate model could be derived from joint inversion of GDS and MT data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora B R 1990 Magnetometer array studies in India: Present status, data interpretation and assessment of numerical modelling results;Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet Sci.) 99 693–716
Arora B R 1993 Implications of electrical conductivity structures in the tectonic framework of northwest India;Curr. Sci. 64 848–855
Arora B R and Mahashabde M V 1987 A transverse conductive structure in the northwest Himalaya;Phys. Earth Planet. Int. 45 119–127
Brewitt-Taylor C R and Weaver J T 1976 On the finite difference solution of two-dimensional induction problems;Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 47 375–396.
Chamalaun F H, Prasad S N, Lilley F E M, Srivastava B J, Singh B P and Arora B R 1987 On the interpretation of the distinctive pattern of geomagnetic induction in northwest India;Tectonophysics 140 247–255
Jacobs D A H 1986 A generalization of the conjugate gradient method to solve complex system;IMA. J. Numer. Anal. 6 447–452
Jones F W and Pascoe L T 1971 A general computer program to determine the perturbation of aternating electric currents in a two-dimensional model of a region of uniform conductivity with an embedded inhomogeneity;J. R. Astr. Soc. 24 3–30
Lilley F E M, Singh B P, Arora B R, Srivastav B J, Prasad S N and Saloane M N 1981 A magnetometer array study in northwest India;Phys. Earth Planet. Int. 232–240
Rastogi A 1997 A finite difference algorithm for two-dimensional inversion of geoelectromagnetic data;Ph.D thesis, Department of Earth Sciences, University of Roorkee, Roorkee
Sarkar T K (ed) 1991Application of conjugate gradient method to electromagnetic and signal analysis, Elsevier Science Publ. Co., Inc.
Singh R P and Pedersen L B 1988, A transverse conductive structure in the northwest Himalaya by B R Arora and M V Mahashabde;Phys. Earth Planet. Int. 53 177–179
Weaver J T 1994Mathematical methods for geo-electromagnetic induction; Research Studies Press, Taunton 316.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rastogi, A., Gupta, P.K. & Niwas, S. Inversion of GDS data of northwest Himalaya using EM2INV. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet Sci.) 107, 149–154 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02840465
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02840465