Abstract
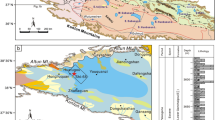
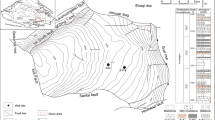
A systematic analysis of the inorganic and organic geochemistry of Middle Permian source rocks comprising carbonate rocks and mudstones was carried out, with samples collected from the outcrop and bore of the Junggar, Turpan and Ili basins in northern Xinjiang. This study confirmed that sedimentary parameters for an ancient water body, such as inorganic geochemistry and paleosalinity, have a close relation to the organic matter of source rocks. It is also disclosed that phytane predominance in the source rocks is mainly due to a reducing environment. Biomarkers, such as gammacerane and β-carotene, in the samples reflect a specific salinity in the sedimentary environments. Sedimentary zones with a strong reducing environment are more likely to produce deposits of primary organic matter, which will be buried and preserved contemporarily. Consequently, the source rocks are generally high in organic content and better in organic type than ordinary ones, and vice versa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carroll A. R. (1998) Upper Permian lacustrine organic facies evolution, Southern Junggar Basin, NW China [J].Org. Geochem. 25, 649–667.
Carroll A. R. and Bohacs K. M. (2001) Lake-type controls on petroleum source rock potential in nonmarine basins [J].AAPG Bull. 85, 1033–1053.
Cheng Keming, Wang Tieguan, Zhong Ningning, and Zhao Shiqing (1995)Geochemistry of Hydrocarbon Source Rocks [M]. pp. 17–40. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese).
China National Petroleum Corporation (1997) «National Petroleum Sector Standard of People’ s Republic of China»SY/T-5125-1996,Identification and Classification of Macérai by Transmitted Light—Fluorescence [M]. pp. 1–12. Petroleum Industry Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese).
Compiling Group of “Petroleum Geology of China” (1993)Petroleum Geology of China (No. 15) [M]. pp. 15–25. Petroleum Industry Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese).
Deng Hongwen and Qian Kai (1993)Sedimentary Geochemistry and Environment Analysis [M]. pp. 95–104. Gansu Science and Technology Press, Lanzhou (in Chinese).
Feng Jianhui, Jiang Zaixing, Lu Hongbo, He Huisheng, Ma Weiming, and Chen Faliang (2000)The Research on Sequence Stratigraphy and Sedimentology in Ili Basin [M]. pp. 22–96. Shandong Petroleum University Press, Dongying (in Chinese).
Genger D. and Sethi P. (1998) A geochemical and sedimentological investigation of high-resolution environmental changes within the late Pennsylvanian (Missourian) endora core black shale of the mid-continent region, U.S.A. In:Shale and Mudstones (1) [M]. pp. 271–293. E. Schweizerbart’ sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Stuttgart.
Geoscience Section of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Xinjiang Petroleum Manage Bureau (1989)The Relation Between the Developing of Basin and Forming of Hydrocarbon in Junggar Basin [M]. pp. 1–85. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese).
Gradsteind F. M. (2005) (Translated by Jin Yugan, Wang Xiangdong, and Wang Yue) International stratigraphic chart [J].Journal of Stratigraphy.29, 97–98.
Hatch J. R. and Leventhal J. S. (1992) Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the Upper Pennsylvanian (Missourian) stark shale member of the Dennis limestone, Wabaunsee County, Kansas, U. S. A. [J].Chemical Geology.99, 65–82.
Hu Xiumian, Wang Chengshan, Li Xianghui et al. (2000) CenomanianTuronian anoxic event in southern Tibet: A study of organic geochemistry [J].Geochimica.29, 417–424 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang Zhusheng (1983) Perhydro carotenes in Karamay crude oil and their geochemical characteristics [J].Oil and Gas Geology.4, 151–159 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Kenneth E. Peters and Michael Moldowan J. (1993)The Biomarker Guide: Interpreting Molecular Fossils in Petroleum and Ancient Sediments (Translated by Jiang Naihuang, Zhang Shuichang, Ling Yonghan, Zhang Dajiang, and Sun Fuqing) [M]. pp. 93–142. Petroleum Industry Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese).
Li Guangyun (2002) Oil-gas geology and exploration target of Hi Basin [J].Xinjiang Geology.20, 72–76 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Xianqing, Hou Dujie, Tang Youjun, Hu Guoyi, and Xiong Bo (2003) Molecular geochemical evidence for the origin of natural gas from dissolved hydrocarbon. I. Ordovician formation waters in central Ordos Basin [J].Chinese Journal of Geochemistry.22, 191–202.
Liu Chunlian, Yang Jianlin, Hans J. R., and Annette S. R. (2001) Factors influencing organic distribution in lacustrine sediments [J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica.19, 113–115 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Guijian, Yang Pengyue, Peng Zicheng, and Wang Guiliang (2003) Comparative study of chemical composition of paragenetic sepropelic coal and humic coal from Zibo Coalfield [J].Geology-Geochemistry.31, 23–27 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Miao Jianyu (1996) Research on Permian-Triassic hydrocarbon source rock in Turpan depression [J].Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition).26, 267–270 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Miao Jianyu, Zhou Lifa, Deng Kunm, Li Jianfeng, and Han Zhongyuan (2004) Sedimentary environment of Permian source rocks in Ili Basin [J].Oil and Gas Geology.25, 294–299 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Peng Jun and Xu Wangguo (2001) Geochemical characteristics of depositional environment of the Upper Sinian bedded siliceous rocks in western Hunan [J].Geochimica.30, 293–298 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Song Yan (1995)The Geology Characteristic of Zone for Gas Accumulation in Junggar Basin [M]. pp. 1–159. Petroleum Industry Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese).
State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision (2002) «National standard of People ’ s Republic of China» GB/T 18602-2001Rock Pyrolysis [M]. pp. 1–8. National Standard Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese).
Su Chuanguo, Li Dingfang, and Jiang Xinyi (2002) Hydrocarbon generation potential of upper Permian source rocks in Taibei depression, Turpan-Hami Basin [J].Xinjiang Geology.20, 77–79 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Yutao (1996) The relations between environmental features of biomarker and oil source [J].Xinjiang Petroleum Geology.17, 130–137 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Zhansheng, Wang Peirong, Lin Renzi, Zhao Hong, Chen Qi, and He Wenxiang (2002) Identification and significance of Δ5-stenols in salty terrestrial sediments [J].Geochimica.31, 206–210 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Xiyong, He Yulong, Wei Youyi, and Yu Hongping (2001) Study on weathering characteristics of black strata [J].Geology-Geochemistry.29, 17–23 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xia Xinyu, Zeng Fangang, and Hong Feng (2001) Hydrocarbon-generating potential of organic matter in epicontinental sea carbonate rocks in China [J].Oil and Gas Geology.22, 287–292 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang Yuangen, Liu Congqiang, Xu Lei, Wu Pan, and Zhang Guoping (2004) Effects of heavy metal contamination on microbial and community structure in soils [J].Chinese Journal of Geochemistry.23, 319–328.
Zhao Bai (1994) The carboniferous and Permian as major oil source rocks in Junggar Basin [J].Xinjiang Petroleum Geology.15, 10–15 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhong Ningning and Qing Yong (1995)Organic Petrology of Carbonate Rocks [M]. pp. 14–33. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese).
Zhu Guangyou and Jin Qiang (2002) Study on source rock heterogeneity—A case study of the Well Niou-38 Dongying depression [J].Acta Petrolei Sinica.23, 34–39 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zu Rukai, Guo Hongli, He Dongbo, Luo Zhong, and Shao Longyi (2002) Geochemical characteristics of carboniferous mudstones in Qilian Mountain and northern Qindam Basin [J].Geology-Geochemistry.30, 45–52 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was funded by the National Key Project ( also known as the 973 Program for Basic Research of China ( Grant No. 2003CB214600).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jianyu, M., Hansheng, K., Lifa, Z. et al. Sedimentary environments of organic matter from Middle Permian source rocks in northern Xinjiang, China. Chin. J. Geochem. 25, 258–265 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02840421
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02840421