Abstract
Generalized equations for the anomalies in any component of the earth’s magnetic field due to two-dimensional bodies of arbitrary magnetization are derived in terms of a new parameter, called the direction of measurement. Schemes for inverting the magnetic anomalies of arbitrarily magnetized dykes and basement topographies are then developed and the relevant computer software is presented. In both the schemes, the initial values of the parameters are calculated by the computer, so that the input merely consists of the anomalies and their distances. The differences in the observed and calculated anomalies are solved iteratively for the errors in initial values of the parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
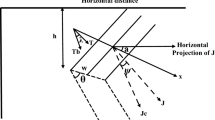
- J:
-
intensity of effective magnetization of the two-dimensional body, lying in a plane perpendicular to the strike
- ϕ:
-
dip of the effective magnetization
- α:
-
strike of the body measured from the magnetic north due east or west
- i:
-
dip of the earth’s magnetic field
- F:
-
earth’s magnetic field, expressed in gammas
- Dm :
-
direction of measurement, the new parameter introduced; it is 0 for the horizontal ΔH, π/2 for vertical ΔV andi for the total field ΔF anomalies
- ΔT :
-
anomaly in any component; it is equal to ΔH, ΔV and ΔF whenD m is 0, π/2 andi respectively
- ΔT cal :
-
calculated anomaly
- DT:
-
ΔT-ΔT cal
- K:
-
susceptibility contrast of the body
- θ:
-
geological dip of the dyke model
- Q:
-
an angle, which is a function of θ, ϕ,D m, i and α
- D:
-
distance from an arbitrary reference to the position of centre of the dyke
- x, X:
-
distance co-ordinates of anomalies
- W:
-
half-width of the dyke
- Z:
-
depth to top of the dyke; mean depth of the basement topography/ magnetic interface
- ZT:
-
depth to the interface or topography
- ΔT max,ΔT min :
-
maximum and minimum anomalies
- X max,X min :
-
positions of maximum and minimum anomalies
References
Gay S Parkar 1963 Standard curves for interpretation of magnetic anomalies over long tabular bodies;Geophysics 28 161–200
Grant F S and West G F 1965Interpretation theory in applied geophysics (New York: McGraw Hill)
Gulatee B L 1938 Magnetic anomalies; Professional paper 29 Survey of India (Dehra Dun)
Radhakrishna Murthy I V 1985 Magnetic equivalence of dipping beds, faults and anticlines, pageoph, V. 13, pp. 839–901
Radhakrishna Murthy I V and Visweswara Rao C 1973 Two methods for computer interpretation of magnetic anomalies dykes;Geophysics 38 710–718
Rao B S R and Murthy I V R 1978Gravity and magnetic method of prospecting (New Delhi: Arnold Heinmann)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murthy, I.V.R. Magnetic anomalies of two-dimensional bodies and algorithms for magnetic inversion of dykes and basement topographies. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet Sci.) 99, 549–579 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02840316
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02840316