Abstract
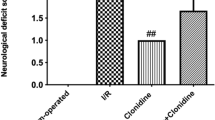
Objective: To investigate muscone’s neuroprotective action and its mechanism in rats with acute cerebral ischemic injury.Methods: Rat focal ischemic model of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) was established by thread inserting method. TTC staining, RT-PCR and Western blot analysis were used to study the effects of muscone on infracted volume, EAAClmRNA and protein levels.Results: Infarcted volume in the muscone treated group was significantly lower than that in the model control group. Compared with normal group, EAAC1 mRNA level increased in the model control group at 6 and 24 hrs, and protein level increased at 24 hrs after modelling, muscone could reduce the increased expression in model rats.Conclusion: Muscone possesses the action of neuroprotection, its mechanism may be related to reduction of EAAC1 and protein expressions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
XIA X, ZHANG YX. Mordern application and research of traditional Chinese medicine-section of internal medicine. Shanghai: Shanghai Traditional Chinese Medical University Press, 1997: 407–409.
JIANG ZY, LI CD, ZHOU D etal. Protection effect of moschus on neuron damage caused by rat’s experimental cerebral ischemia. Chinese Journal of Traditional Medical Science and Technology 2001;8(2): 96–97
JI YB. Pharmacological action and application of available composition of traditional Chinese medicine. Haerbing: Heilongjiang Scientific and Technical Press, 1995: 313–315.
Yukio Nishizawa. Glutamate release and neuronal damage in ischemia. Life Science 2001;69(4): 369–381
Danbolt NC. Glutamate uptake. Progress in Neurology 2001;65(1): 1–105.
David JR. Takeo Oshima, David A. Glutamate in severe brain ischemia is mainly by reversed uptake. Nature 2000, 403(6767): 316–321
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rat. Stroke 1989; 20: 84–91.
Derugin N, Wendland M, Muramatsu K, et al. Evolution of brain injury after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in neonatal rats. Stroke 2000; 31 (7): 1752–1761.
Li Tao, Daiwei Shen, Sujay Pandey, et al. Structure and developmental expression of the mouse RGR opsin gene. Molecular Vision 1998;4: 25–30.
MO QZ, GONG B, MAO HM, et al. The absorption, distribution and excretion of3H-muscone in the body. Research of Chinese traditional patent medicine 1984; (7): 1–4.
Knai Y, Trotti D, NussbergerS, et al. The high-affinity glutamate transporter family. In: Reith MEA ed. Neurotransmitter Transporters: Structure, Function and regulation. New Jerey: Human Press, 1997: 171–181.
Dube GR, Marshall KC. Modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission in locus coeruleus by multiple presynaptic merabotropic glutamate receptors. Neuroscience 1997;80: 511–521.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by the fund of “Hundred Persons Project” of Shanghai Public Health Bureau (No. 97BR016)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hui, L., Hu, C., Yin, G. et al. Effect of muscone on neuronal glutamate transporter EAAC1 expression in rats with acute cerebral ischemia. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 9, 285–288 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02838617
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02838617