Abstract
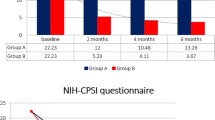
Objective: To evaluate the clinical efficacy of Qianlie’an (QLA) suppository via anal route administration in treating chronic prostatitis syndrome.Methods: A randomized open-labelled prospective controlled trial was carried out. The total of 120 patients with chronic prostatitis syndrome were randomly divided into 2 groups: 60 patients in the treated group who were treated with QLA suppository combined with ofloxacin, and the other 60 patients in the control group who were given ofloxacin alone. The efficacy was evaluated by WBC count in the expressed prostatic secretion (EPS) and the Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (CPSI) made by the National Institute of Health (NIH). The clinical effects were also observed in a 4-week follow-up.Results: All but six cases completed the trial and the follow-up. It showed that in the treated group recovery rate was 17. 2%, markedly effective rate 34. 5%, effective rate 32. 8%, total markedly effective rate 51. 7%, and total effective rate 84. 5%, all of which were superior to those in the control group (total markedly effective rate 32.1% and total effective rate 66.1%, respectively),P < 0.01.Conclusion: Administration of QLA suppository via anal route combined with oral antibiotics is an effective therapy for chronic prostatitis syndrome. It can relieve the symptoms of chronic prostatitis syndrome markedly and rapidly. It is a new choice for treatment of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shafik A. Anal submucosal injection; a new route for drug administration. VI. Chronic prostatitis: a new modality of treatment with report of eleven cases. Urology 1991; 37(1): 61–64.
Krieger JN, Nyberg L Jr and Nickel JC. NIH consensus definition and classification of prostatitis. JAMA 1999; 282: 236–237.
Alexander RB, Trissel D. Chronic prostatitis: results of an internet survey. Urology 1996; 48: 568–574.
Nickel JC, Johnston B, Downey J, et al. Pentosan polysulfate therapy for chronic nonbacterial prostatitis (chronic pelvic pain syndrome category III A): a prospective multicenter clinical trial. Urology 2000; 56: 413–417.
LIN CR, WANG M, LIU JX. Study on pharmacokinetics of Qianlie’an suppository in rats. Natl J Androl 2000; 6(2): 107–110.
Fukuda K, Hibiya Y, Mutoh M, et al. Inhibition by berberine of cyclooxygenase-2 transcriptional activity in human colon cancer cells. J Ethnopharmacol 1999; 66(2): 227–233.
JIANG MX, YAO WX, LING BD, et al. Blocking action of berberine on adrenoceptors in rat vas deferens and anococcygeus muscle. Acta Pharmacol Sin 1986; 7(6): 511–515.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jun-ping, X., Xing-fa, C., Zhi-shang, Y. et al. Effects of Qianlie’an suppository in patients with chronic prostatitis syndrome: A randomized open-labelled prospective and controlled trial. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 9, 195–198 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02838031
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02838031