Abstract
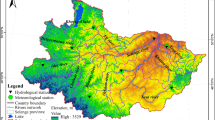
The environment evolution of Wuliangsuhai wetland since 1986 is analyzed based on the remote sensing principle. The total water area of Wuliangsuhai lake has been increased during the past 17 years. The open water area had an increasing trend before 1987, and the trend was decreasing up to 1996, then the trend has increased again since 2000; the variation of the water area with dense aquatic weed is basically contradictory to the variation of open water area. The natural reed area had been decreased before 1987, and then it has been increased. The areas of shallow water and swamp have been slightly increased, in fact, the variations are quite steady. The artificial reed area has been increased since the reed plantation was started in 1988. The relationships of the water environment, the climate, hydrology and different types of areas are discussed, and then the technological measures for sustainable development and utilization of Wuliangsuhai lake water environment are proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai Xue, Lu Nanjun, 1994. Study of the spatial and time variation of the water quality parameters of Boyang lake.Water Resources Science and Technology of Jiangxi, 20(2): 181–188. (in Chinese)
Environment Monitoring General Station of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. The Report of Environment States of IMAR in 1999 to 2002, 1999 to 2002. (in Chinese)
Jin Shengao, Jiang Shirong, 2001. Hydrological characteristics of Dongting Lake outlet.Water Resources and Hydropower Express, 22(18): 23–26. (in Chinese)
Liu Xiaoyuan, 2001. The analysis of the water level of Qinghai Lake.Arid Zone Research, 18(3): 58–62. (in Chinese)
Shang Shiyou, Du Jianmin, Li Xuying, 2003. Study on the management of eutrophication in Wuliangsuhai.Journal of Inner Mongolia Agriculture University, 24(4): 6–12. (in Chinese)
Wang Limping, Chen Yaxin, Zeng Guofang, 1993. Irrigation and Drainage, the Saline and Alkaline Control of Hetao Irrigation Area of IMAR. Beijing: Water Resources and Hydropower Publisher, (in Chinese)
Zhu Yan, Cui Guangbo, 2001. Causes of shrinking and drying up of Qinghai Lake, trend of development and its impact on ecological environment.Journal of Hehai University, 29(4): 104–108. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruihong, Y., Changyou, L., Tingxi, L. et al. The environment evolution of Wuliangsuhai wetland. J. Geogr. Sci. 14, 456–464 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02837489
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02837489