Abstract
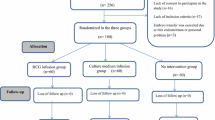
Objective: To study the effect of Chinese herbal medicine Gutai Decoction (GTD) on the abortion rate ofin vitro fertilization and embryo transfer (IVF-ET).Methods: Observed were two hundred and forty-seven women having received IVF-ET and with β-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-HCG) > 25 IU/L on the 14th day after transferring. All were treated conventionally with progesterone 20 –80 mg per day after transferring and if necessary the treatment was supplemented with Progynova 2 –4 mg per day, with the medication withdrawn gradually from the 9th week of pregnancy till stopped completely. Among them 131 cases received GTD medication additionally, for 109 cases of whom the medication started from the 2nd day of transferring (taken as Group A) and for the other 22 cases from the 14th day after transferring (taken as Group B), the other 116 cases with no additional GTD treatment given were taken as the control group, with the medication lasting to the 12th week. The abortion rate in them was observed.Results: The abortion rate in Group A, Group B and the control group was 12.84%, 13.64% and 23.28%, respectively, the difference between the GTD treated groups and the control group was significant (P < 0.05).Conclusion: Chinese medicine GTD could reduce abortion rate in women receiving IVF-ET.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luo LL, editor. Sterility and infertility. 1st ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2000: 287–294.
Zhang XJ. Effect of Huataiyin on rat’s uerine smooth musclesin vitro and its fetal protection. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae 1996; 2 (6): 48.
Li GW. Effect and pharmacological study on Jiawei Shoutaiwan in treating habitual abortion. J Tradit Chin Med 1988;33(4): 6.
Qi GC. Taiyuanyin and Hutaiwan in treating 64 cases of threatened abortion. Liaoning J Tradit Chin Med 1996;23(5): 218.
Gui SQ, Xu J, Yu EG, et al. Deficiency of blocking antibody of spontaneous abortion treated by traditional Chinese medicine. J Shanghai Med Univ 1997;24(3): 217–219.
Agrawal SK, Wisot AL, Garzo G, et al. Cornai pregnancies in patients with prior salpingectomy undergoingin vitro fertilization and embryo transfer. Fertil Steril 1996;66(4): 652–659.
Paltieli Y, Eibschitz I, Ziskind G, et al. High progensterone levels and ciliary dysfunction: a possible cause of ectopic pregnancy. J Assist Reprod Genet 2000;17(2): 103–106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Guangdong Province (No. 403027)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ying, L., Jing-zhi, W. Effect of Gutai Decoction on the abortion rate ofin vitro fertilization and embryo transfer. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 12, 189–193 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02836520
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02836520