Abstract
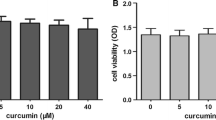
Objective: To investigate the molecular mechanisms and effective target ponits of lipid-lowering drug, Rhizoma Curcumae Longae, and study the effect of curcumin on the expression of low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptors in macrophages in mice.Methods: Macrophages in mice were treated with curcumin, which was purified from the ethanolly extraction of Rhizoma Curcumae Longae for 24 h. The LDL receptors expressed in the macrophages were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and assay of Dil labeled LDL uptake by flow cytometer.Results: It was found for the first time that 10 μmol/L-50 μmol/L curcumin could obviously up-regulate the expression of LDL receptor in macrophages in mice, and a dose-effect relationship was demonstrated.Conclusion: One of the lipid-lowering mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine, Rhizoma Curcumae Longae, was completed by the effect of curcumin through the up-regulation of the expression of LDL receptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guis S, Bendahan D, Kozak Ribbens G, et al. Rhabdomyolysis and myalgia associated with anti-cholesterolemic treatment as potential signs of malignant hyperthermia susceptibility. Arthr Rheum 2003;49(2): 237–238.
Gaist D, Jeppesen U, Andersen M, et al. Statins and risk of polyneuropathy: a case control study. Neurology 2002: 58(9): 1333–1337.
Brown MS, Goldstein JL. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science 1986;232(4746): 34–47.
Soni KB, Kuttan R. Effect of oral curcumin administration on serum peroxides and cholesterol levels in human volunteers. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1992;36(4): 273–275.
Soudamini KK, Unnikrishnan MC, Soni KB. Inhibition of lipid peroxidation and cholesterol levels in mice by curcumin. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1992;36(4): 239–243.
Babu PS, Srinivasan K. Hypolipidemic action of curcumin, the active principle of turmeric (Curcuma longa) in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Mol Cell Biochem 1997;166(1–2): 169–175.
Sreejayan, Rao MN. Curcuminnoids as potent inhibitors of lipid peroxidation. J Pharm Pharmacol 1994;46(12): 1013–1016.
Barak LS, Webb WW. Fluorescent low density lipoprotein for observation of dynamics of individual receptor complexes on cultured human fibroblasts. J Cell Biology 1981;90: 595–604.
Brown MS, Goldstein JL. The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell 1997;89 (3): 331–340.
Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Molecular medicine. The cholesterol quartet. Science 2001;292(5520): 1310–1312.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chun-lei, F., Ying, Q., Xing-de, W. et al. Effect of curcumin on the gene expression of low density lipoprotein receptors. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 11, 201–204 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02836505
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02836505