Abstract
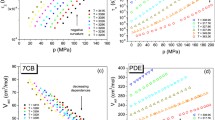
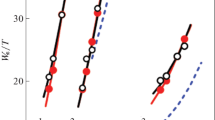
A mechanical model of liquid crystals (LCs) was used to explain the phase formation and thermal properties. The LC phases in the model are micro-machine systems consisting of an ensemble of molecular rotors, and some dynamic parameters in a semi-experiment molecular orbit method. A novel explanation on the multi-phase formation of LC system is obtained. It is found that the value of the critical rotational velocity is a key parameter for the characterization of each homologous series. The dipole moment of the molecules was also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K Toriyama and D A Dunmur. A Molecular Model for the Smetic B Phase-the Stabilized Molecular Rotor.Liq. Cryst., 1993, 13:797–810
K Toriyama, H Kimura and H Onnagawa. Mechanical String Model for Liquid Crystal Ensemble: A Comprehensive Model for Polymorphism.Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2001, 40:5000–5007
J Xu, H Okada, H Onnagawa, S Sugimori and K Toriyama. Liquid Crystal System as Molecular Machinery: Investigation of Dynamic Impedance Matching Between Molecular Core and Terminal Groups Using Rotor-Bearing Model.Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2000, 39:1801–1807
H Ma, J Xu, H Okada, S Sugimori, H Onnagawa and K Toriyama. Mechanical Rotor Model for Fluorinated Terphenyl Liquid Crystals.Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2004, 4A, 43:148–171
H Ma, H Okada, S Sugimori, H Onnagawa and K Toriyama. A Mechanical Model Study on Correlations of Liquid Crystal Phase and Dynamic Parameters in Linear Molecules.Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2004, 5A, 43:2626–2627
R Gasch, H Pfuytzner.Rotordynamik, Eine Einfuhrung. Berlin Springer-Verlag, 1975 [in German]
D Demus, J Goodby, G W Gray, H-W Spiess and V Vill.Handbook of Liquid Crystals. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 1998
S Mitra, R Mukhopadhyay, K Venu. Molecular Motions in Liquid Crystal BBBA (40.4): QENS Study.Chemical Physics, 2000, 261:149–156
An J, Min X M, Nan C W, Cai K F. Structural Characteristics and Quantum Chemistry Calculation of Al-Doped Boron Carbides.J. Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2000, 15(3):27–32
Min X M, Xiao R J, Wang Han, Wang Wei-min. Electronic Structure and Chemical Band of Titanium Diboride.J. Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2003, 18(2):11–14
B K Sadashiva, G S R S Rao. A Convenient Method for the Preparation of 4-n-alkyl-4″-cyano-p-terphenyl.Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst., 1977, 38:345–352
A J Leadbetter, P A Tucker, G W Gray, A R Tajbakhsh. Unusual structures in some alkyl cyanoterphenyls.Liq. Cryst., 1990, 8:1–12
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the Key Technologies R and D Programme of Henan Province (No. 001120321)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhenxin, L., Heng, M. & Shipu, L. Relationship between multi-phase formation and molecular structure for liquid crystal system. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 20, 11–13 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02835015
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02835015