Abstract
This paper investigates the functioning of mitochondrial energy-producing machinery in cold-induced edema and the level of energy charge available within the cell for cation transport.
Direct measurements of mitochondrial ATP production in vasogenic brain edema are carried out by testing different metabolic pathways.
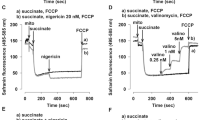
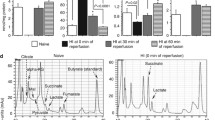
In our model (freezing lesion edema), substrate level phosphorylation is not affected by the cold injury. However, when the respiratory substrates are glutamate + malate or pyruvate + malate, the inhibition of ATP production in mitochondria isolated from edematous cells reflects the decrease of oligomycin-sensitive ATPase. The larger inhibition of the succinate dehydrogenase activity seems to affect only the phosphorylations coupled to succinate oxidation.
Alternative transmembranal metabolic pathways (i.e., aspartate-malate shuttle, pyruvate cycle) bypassing the step might be operating in these edematous cells and play an important energetic role. Indeed, under in vivo conditions, the energy charge remains normal and the ATP/ADP ratio higher than normal during edema expansion.
These results are consistent with a large decrease in Na+, K+-ATPase function (Rigoulet et al., 1979), which normally uses an important part of available ATP.
We conclude that the development of intracellular edema is caused by the breakdown of Na+, K+-ATPase and not by a shortage of high energy compounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AdN:
-
adenylic nucleotides
- CCCP:
-
carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone
- 2,6-DCIP:
-
2,6-dichlorophenol indophenol
- Pi :
-
inorganic phosphate
- PMS:
-
phenazine methosulfate
- iCBF:
-
regional cerebral blood flow
- TCA:
-
trichloroacetic acid
References
Atkinson D. E. (1968) The energy charge of the adenylate pool as a regulatory parameter. Interaction with feedback modifiers.Biochemistry,7, 4030–4034.
Berry M. N. (1980) The function of energy-dependent redox reactions in cell metabolism.FEBS Lett. suppl. 117, K106-K120.
Blakemore W. F. (1971) The ultrastructural appearance of astrocytes following thermal lesions of the rat cortex.J. Neurol. Sci. 12, 319–332.
Borst P. (1963) Hydrogen transport and transport. inFunctionnelle und Morphologische Organization der Zelle (Karlson P., ed.), pp. 137–162, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Clark J. B. and Nicklas W. J. (1970) The metablism of rat brain mitochondria: preparation and characterization.J. Biol. Chem. 245, 4724–4731.
Demopoulos H. B., Flamm E. S., Seligman M. L., Mitamura J. A., and Ransohoff J. (1979) Membrane perturbations in central nervous system injury: theoretical basis for free radical damage and a review of the experimental data. InNeural Trauma (Popp A.J., Bourke R.S., Nelson L.R., and Kimelberg, H.K., eds.), pp. 63–78. Raven Press, New-York.
Dennis S. C. and Clark J. B. (1978) The regulation of glutamate metabolism by tricarboxylic acid cycle activity in rat brain mitochondria.Biochem. J. 172, 155–162.
Frei H. J., Wallenfang Th., Poll W., Reulen H. J., Schubert R., and Brock M. (1973) Regional cerebral flow and regional metabolism in cold-induced edema.Acta Neurochir. 29, 15–28.
Go K. G., Zijlstra W. G., Flanderijn H., and Zuiderveen F. (1974) Circulatory factors influencing exudation in cold-induced cerebral edema.Exp. Neurol. 42, 332–338.
Golberg N. D., Passonneau J. V., and Lowry O. H. (1966) Effects of changes in brain metabolism on the levels of citric acid cycle intermediates.J. Biol. Chem. 241, 3997–4003.
Grote J., Reulen H. J., and Schubert R. (1978) Increased tissue water in the brain influence on regional cerebral blood flow and oxygen supply.Adv. Neurol. 20, 333–339.
Holian A., Owen C. S., and Wilson D. F. (1977) Control of respiration in isolated mitochondria: quantitative evaluation of the dependence of respiratory rates on (ATP), (ADP) and (Pi).Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 181, 164–171.
Holian A. and Wilson D. F. (1980) Relationship of transmembrane pH and electrical gradients with respiration and ademine 5′-triphosphate synthesis in mitochondria.Biochemistry 19, 4213–4221.
Keesey J. C. and Wallgren H. (1965) Movements of radioactive sodium in cerebral cortex slices in response to electrical stimulation.Biochem. J. 95, 301–310.
Klatzo I., Wisniewski H., and Smith D. E. (1965) Observations on penetration of serum proteins into the central nervous system. InProgress in Brain Research, Vol. 15, Biology of Neuroglia (De Robertis E. D. P. and Carrea R., eds.) pp. 73–88, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Klatzo I. (1967) Neuropathological aspects of brain edema.J. Neuropath. Exp. Neurol. 26, 1–14.
Klatzo I., Chui E., Feijiwara K., and Spatz M. (1980) Resolution of vasogenic brain edema. InAdvances in Neurology, Vol. 28, Brain Edema (Cervos-Navarro J. and Ferszt R., eds.) pp. 359–373, Raven Press, New York.
Lee J. C. and Bakay L. (1966) Ultrastructural changes in edematous central nervous system.Arch. Neurol. 14, 36–49.
Ljunggren B., Schutze H., and Siesjö B. K. (1974) Changes in energy state and acid-base parameters of the rat brain during complete compression ischemia.Brain Res. 73, 277–289.
Lowry O. H., Passonneau J. V., Hasselberger F. X., and Schulz H. (1964) Effect of ischemia on known substrates and cofactors of the glycolytic pathway in brain.J. Biol. Chem. 239, 18–30.
Lundin A., Richardsson A., and Thore A. (1976) Continuous monitoring of ATP-converting reactions by purified firefly luciferase.Anal. Biochem. 75, 611–620.
Marmarou A., Takagi H., and Shulman K. (1980) Biomechanics of brain edema and effects on local cerebral blood flow. in:Advances in Neurology, Vol. 28, Brain Edema (Cervos-Navarro J. and Ferszt R., eds.), pp. 345–358, Raven Press, New York.
Meijer A. J. and Van Dam K. (1974) The metabolic significance of anion transport in mitochondria.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 364, 213–244.
Nelson S. R. and Mantz M. L. (1971) Energy reserve levels in edematous mouse brain.Exp. Neurol. 31, 53–59.
Nicholls D. G. and Bernson S. M. (1977) Interrelationships between proton electrochemical gradient, adeninenucleotide phosphorylation potential and respiration, during substrate level and oxidative phosphorylation by mitochondria from brown adipose tissue of cold-adapted guinea-pigs.Eur. J. Biochem. 75, 601–612.
Ozawa K., Itada N., Kuno S., Seta K., Handa H., and Araki C. (1966) Biochemical studies on brain swelling. I. Changes in respiratory control, 2,4-dinitrophenol induced ATPase activity and phosphorylation. Correlation between brain swelling and mitochondrial function.Folia Psychiatr. Neurol. Japonica 20, 57–72.
Reulen H. J., Medzihrady F., Enzenbach R., Marguth F., and Brendel W. (1969) Electrolytes, fluids, and energy metabolism in human cerebral edema.Arch. Neurol. 21, 517–525.
Reulen H. J. (1976) Vasogenic brain edema. New aspects in its formation, resolution and therapy.Br. J. Anaesth. 48, 741–752.
Ridge J. W. (1972) Hypoxia and the energy charge of the cerebral adenylate pool.Biochem. J. 127, 351–355.
Rigoulet M., Guerin B., Cohadon F., and Vandendriessche M. (1979) Unilateral brain injury in the rabbit: reversible and irreversible damage of the membranal ATPases.J. Neurochem. 32, 535–541.
Robinson B. H., Williams G. R., Halperin M. L., and Leznoff C. C. (1971) The sensitivity of the exchange reactions of tricarboxylate, 2-oxoglutarate and dicarboxylate transporting systems of rat liver mitochondria to inhibition by 2-pentylmalonate,p-iodobenzylmalonate and benzene 1,2,3-tricarboxylate.Eur. J. Biochem. 20, 65–71.
Rosenthal M., Martel D., Lamanna J. C., and Jobsis F. F. (1976)In situ studies of oxidative energy metabolism during transient cortical ischemia in cats.Exp. Neurol. 50, 477–494.
Sato K., Yamaguichi M., Mullan S., Evan J. P., and Ishii S. (1969) Brain edema a study of biochemical and structural alterations.Arch. Neurol. 21, 413–424.
Singer T. P., Rocca E. and Kearney E. B. (1966) Fumarate reductase, succinate and NADH dehydrogenase of yeast: properties and biosynthesis. InFlavins and Flavoproteins (Slater B. C., ed.), pp. 391–426, Elsevier, Amsterdam, London, New York.
Sutton L. N., Welsh F., and Bruce D. A. (1980) Bioenergetics of acute vasogenic edema.J. Neurosurg. 53, 470–476.
Veech R. L., Lawson J. W. R., Cornell N. W., and Krebs H. A. (1979) Cytosolic phosphorylation potential.J. Biol. Chem. 254, 6538–6547.
Whittam R. (1962) The dependence of the respiration of brain cortex on active cation transport.Biochemistry 82, 205–212.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rigoulet, M., Averet, N. & Cohadon, F. Energy-producing machinery in vasogenic brain edema. Neurochemical Pathology 1, 43–57 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02834131
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02834131