Abstract
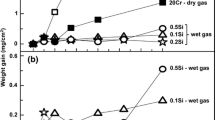
Passive SiO2 films that inhibit undesirable nitrogen uptake form on the surface of stainless steel during bright annealing in H2-N2 atmospheres. The SiO2 films can form at H2O/H2 ratios that are reducing to Cr in the alloy. Algebraic expressions were thermodynamically derived to predict the minimum H2O/H2 ratios required for forming SiO2 (to inhibit nitriding) and the maximum H2O/H2 ratios allowed for preventing formation of Cr2O3 (to prevent surface dulling), as functions of annealing temperature and concentrations of the elements in stainless steels. Predicted results agreed well with observed laboratory and field test data obtained over a range of annealing temperatures and H2O/H2 ratios for stainless steels with varying Si levels. This understanding of the surface chemistry can be used to improve control of H2-N2 annealing atmospheres to inhibit nitriding and prevent surface dulling. In addition, the literature suggests that SiO2 films that inhibit nitrogen uptake during annealing will also improve subsequent corrosion resistance of annealed parts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Grutzner. “Intergranular Corrosion Sensitivity of Nitrogen Containing Austenitic Chromium-Nickel Steels Caused by Chromium Nitride Precipitation,”Stahl und Eisen, Vol 93, 1973, p. 9.
H.J. Grabke. “The Kinetics of Nitriding Steel as a Function of the Oxygen Activity in the Gas Phase,”Archiven Eisenùttenwesens, Vol 44, 1973, p. 603.
H. Zitter and L. Habel. “On the Solubility of Nitrogen in Pure Iron and in Austenitic Chromium-Nickel Steels,”Archiven Eisenùttenwesens, Vol 44, 1973, p. 181.
N.K. Koebel. “Surface Activation in the Heat Treatment of Metals,”Heat Treating, December 1977, p. 14.
N.K. Koebel. “The Role of Externally Prepared Furnace Atmospheres,”Iron and Steel Engineer, July 1964, p. 81.
R.H. Shay and T.L. Ellison. “Inhibited Annealing of Ferrous Metals Containing Chromium,” US patent 4334938.
T.L. Ellison, R.H. Shay, and K.R. Berger. “Selecting Atmospheres for Bright Annealing Stainless,”Metal Progress, June 1983, p. 37.
J.F. Kirner, E.J. Karwacki, and A.L. Cabrera. “Surface Analysis of Austenitic Stainless Steel Annealed in N2-H2 Atmospheres,”Applied Surface Science, Vol 32, 1988, p. 239.
J.F. Kirner, M.R. Anewalt, E.J. Karwacki, and A.L. Cabrera. “Inhibition of Nitrogen Uptake by SiO2 Surface Films Formed on Stainless Steel During Annealing in H2/N2 Atmospheres,”Metallurgical Transactions A, Vol. 19A, 1988, p. 3045.
S. Mrowec and T. Werber. “Gas Corrosion of Metals,” NTIS Report No. TT 76-54038, 1978.
J.W. Brockington, A.L. Cabrera, C.G. Coe, and J.F. Kirner. “Bright Annealing of Stainless Steels,” US patent 4744837.
O. Kubaschewski and C.B. Alcock.Metallurgical Thermochemistry, 5th Ed., Pergamon Press, New York, 1979.
T. Yamazaki, T. Zaizen, S. Asami, and T. Somura. “The Effects of Mn and Si Contents on the Crystal Structure of Oxide films and their Corrosion Protection for Bright-Annealed 430 Ferritic Stainless Steel,”Tetsu to Hagane [Iron and Steel], Vol 69, 1983, pp. 126–35.
T.L. Ellison, Private communication, APCI field test data.
R.H. Shay, Private communication, APCI laboratory data.
H.W. Grunling and R. Bauer. “The Role of Silicon in Corrosion-Resistant High Temperature Coatings,”Thin Solid Films, Vol 95, 1982, p. 3.
D.H. Ro and E. Klar. “Corrosion Behavior of P/M Austenitic Stainless Steels,”Modern Developments in Powder Metallurgy, Vol 13, H.H. Hausner and P.W. Taubenblat, eds., MPIF, Princeton, New Jersey, 1980, p. 247.
S. Ito, H. Omata, T. Murata, and M. Yabumoto. “Atmospheric Corrosion and Development of Stainless Steel Alloy Against Marine Environments,”Degradation of Metals in the Atmosphere, ASTM STP 965, S.W. Dean and T.S. Lee, eds., ASTM, Philadelphia, 1988, pp. 68–77.
T. Murata, E. Ito, H. Komata, K. Takimoto, N. Kobayashi, and M. Yabumoto. “Rust Resistant Stainless Steel and Its Production Method,” Japanese Patent 86042783-B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirner, J.F., Cabrera, A.L. Thermodynamic control of H2-N2 bright annealing atmospheres to inhibit nitrogen uptake by stainless steel. J. Heat Treating 7, 27–33 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02833185
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02833185