Abstract
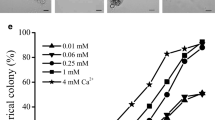
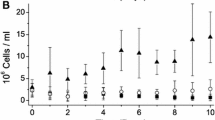
The photosynthetic activities between two main developmental stages, colony and hormogonium, of the edible cyanobacteriumNostoc sphaeroides Kützing, were compared. Hormogonia have a higher content of chlorophyll than that of colonies. It showed that the ratios of phycocyain (PC), allophycocyain (APC) and phycoerythrocyanin (PEC) in hormogonia and colonies were different. The room temperature chlorophyll fluorescence, 77 K chlorophyll fluorescence, measurements of PS I and PS II activities all showed that colony has higher photosynthetic competence than hormogonia. Hormogonia had a higher respiration rate were very close. The responses of hormogonia and colonies to high light illuminations also were different. Both of their oxygen evolution rates decreased quickly with the prolonged high light illumination, but hormogonia can keep relatively higher PS II activity (F v/F m) than that of colonies. The results suggested that colony was photosynthetically more competent than hormogonia, while the ability of hormogonia to tolerate high light illumination was higher than that of colony.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li D H, Liu Y D, Song L R. Hormogonia Mass Differentiation fromNostoc Sphaeroides and the Comparison of Structural Characteristics between Hormogonia and Vegetative Filaments.Phycol Res, 2001,49:81–87.
Campbell E L, Meeks J C. Characteristics of Hormogonia Formation by SymbioticNostoc spp. in Response to the Presence ofAnthoceros punctatus or its Extracellular Products.App Envir. Microbiol, 1989,55:125–131.
Damerval T, Guglielmi G, Houmard J,et al. Hormogonia Differentiation in the CyanobacteriumCalothrix: A Photoregulated Developmental Process.Plant Cell, 1991,3:191–201.
Campbell D, Houmard J, Tandeau de Marsac N. Electron Transport Regulates Cellular Differentiation in Cyanobacteria.Plant Cell, 1993,5:451–463.
Potts M.Nostoc. In: Whitton B A, Potts M, Eds.The Ecology of Cyanobacteria. Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2000. 465–504.
Bilger W, Budel B, Mollenhauer R,et al. Photosynthetic Activity of Two Developmental Stages of aNosotc Strain (Cyanobacteria) Isolated fromGeosiphon pyriforme (Mycota).J Phycol 1994,30:225–230.
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury J B,et al. Generic Assignments, Strain Histories and Properties of Pure Cultures of Cyanobacteria.J Gen Microbiol 1979,111:1–61.
Shi T, Cunningham F X, Youmans M,et al. Cytochromef Loss in Astaxanthin-Accumulating Red Cells ofHaematococcus pluvialis (Chlorophyceace): Comparison of Photosynthetic Activity, Photosynthetic Enzymes, and Thylakoid Membrane Polypeptides in Red and Green Cells.J Phycol, 1995,31:897–905.
Siegelman H W, Kycia J H. Algal biliproteins. In: Hellebust J A, Craigie J S, Eds.Handbook of Phycological Methods: Physiological and Biochemical Methods. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1979.
Zhang Jing-ming, Zhao Jin-quan, Jiang Li-jin,et al. Energy Transfer Kinetics of Phycoerythrocyanin Trimer from CyanobacteriumAnabaena variabilis (II).Science in China, Series C: Life Sciences, 1998,41:133–138 (Ch).
Zhang Jing-ming, Zhao Jin-quan, Jiang Li-jin. Studies on the Mechanism of Energy Transferring in Phycobilisome-Thylakoid Complex: I. the Light State Transition Technology and the Spectra Unfolding Methods.Chinese Science Bulletin, 1997,42:2296–2300 (Ch).
Nakajima Y, Udea R. Improvement of Photosynthesis in Dense Microalgal Suspension by Reduction of Light Harvesting Pigments.J Appl Phycol, 1997,9:503–510.
Nakajima Y, Udea R. Improvement of Microalgal Photosynthetic Productivity by Reducing the Content of Light Harvesting Pigments.J Appl Phycol, 1999,11:195–201.
Nakajima Y, Tsuzuki M, Ueda R. Reduced Photoinhibition of a Phycocyanin-Deficient Mutant ofSynechocystis PCC 6714.J Appl Phycol, 1999,10:447–452.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by the Key Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX1-SW-12), the 973 Project (2002CB412306) and the Frontier Sciences Projects Program of the Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (220316)
Biography: LI Dun-hai (1971-), male, Ph.D., Associate professor, research direction: algal biology and ecosystem restoration.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dun-hai, L., Lan-zhou, C., Gen-bao, L. et al. Comparison of the photosynthetic characteristics of two developmental stages inNostoc sphaeroides Kützing (cyanophyta). Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 10, 931–935 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02832441
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02832441
Key words
- chlorophyll fluorescence
- colony
- hormogonia
- developmental stage
- Nostoc sphaeroides Kütz
- photosynthetic competence