Abstract
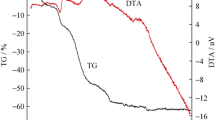
Lithium iron phosphate coated with carbon (LiFePO4/C) was synthesized by improved solid-state reaction using comparatively lower temperature and fewer sintering time. The carbon came from citric acid, which acted as a new carbon source. It was characterized by thermogravimetry and differential thermal analysis (TG/DTA), X ray diffractometer (XRD), Element Analysis (EA) and Scanning electron microscope (SEM). We also studied the electrochemical properties of the material. The first discharge capacity of the LiFePO4/C is 121 mAh·g−1 at 10 mA·g−1, at room temperature. When the current density increased to 100 mA·g−1, the first discharge capacity decreased to 110 mAh·g−1 and retained 95% of the initial capacity after 100 cycles. The LiFePO4/C obtained shows a good electrochemical capacity and cycle ability at a large current density.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Padhi A K, Nanjundaswamy K S, Goodenough J B. Phospho-Olivines as Positive-Electrode Materials for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries.Journal of The Electrochem Society, 1997,144:1188–1194.
Prosini P P, Lisi M, Zane D,et al. Determination of the Chemical Diffusion Coefficient of Lithium in LiFePO4.Solid State Ionics, 2002,148:45–51.
Takahashi M, Tobishima S, Takei K,et al. Characterization of LiFePO4 as the Cathode Material for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries.Journal of Power Sources, 2001,97–98:508–511.
Takahashi M, Tobishima S, Tokei K,et al. Reaction Behavior of LiFePO4 as a Cathode Material for Rechargeable Lithium ion Batteries.Solid State Ionics, 2002,148:283–289.
Anderson A S, Kalska B, Häggström L,et al. Lithium Extration/Insertion in LiFePO4: an X-ray Diffraction and Mossbauer Spectroscopy Study.Solid State Ionics, 2000,130:41–52.
Franger S, Cras F Le, Bourbon C,et al. Comparison Between Different LiFePO4 Synthesis Routes and their Influence its Physico-Chemical Properties.Journal of Power Sources, 2003,119–121:252–257.
Huang H, Yin S C, Nazar L F. Reducing Carbon in LiFePO4/C Composite Electrodes to Maximize Specific Energy, Volumetric Energy, and Tap Density.Journal of The Electrochem Society, 2002,149(9):A1184-A1189.
Yang S F, Zavalij P Y, Whittingham M S. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Lithium Iron Phosphate Cathodes.Electrochemistry Communications, 2001,3:505–508.
Higuchi M, Katayama K, Azuma Y,et al. Synthesis of LiFePO4 Cathode Material by Microwave Processing.Journal of Power Sources, 2003,119–121:258–261.
Franger S, Cras F L, Bourbon C,et al. FePO4 Synthesis Routes for Enhanced Electrochemical Performance.Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2002,5(10):A231-A233.
Prosini P P, Zane D, Pasquali M. Improved Electrochemical Performance of a LiFePO4-Based Composite Cathode.Electrochimica Acta, 2001,46:3517–3523.
Yang S F, Song Y N, Ngala K,et al. Performance of LiFePO4 as Lithium Ion Battery Cathode and Comparison with Manganese and Vanadium Oxides.Journal of Power Sources, 2003,119–121:239–246.
Tang Hao, Feng Chuan-qi, Fan Quan,et al. Synthesis and Electrochemical Properties Yttrium-Doped Spinel LiMn2−yO4 Cathode Material.Chemistry Letters, 2002, 822–823.
Feng Chuang-qi, Tang Hao, Zhang Ke-li,et al. Synthesis and Clectrochemical Characterization of Spinel Phase (Lix−Mn1.93Y0.02O4) for Lithium Ion Battery Applications.Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2003,80:573–576.
Tang Hao, Xi Mei-yun Huang Xi-ming,et al. Rheological Phase Reaction Synthesis of Lithium Intercalation Materials for Rechargeable Battery.Journal of Materials Science Letters, 2002,21:999–1001.
Streltsov A, Belokneva L, Tsirelson G,et al. Multipole Analysis of the Electron Density of Triphylite LiFePO4, Using X-ray Differaction Data.Acta Cryst, 1993,B49:147–153.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20071026)
Biography: ZHOU Xin-wen (1980-), male, Master, research direction: inorganic material chemistry.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xin-wen, Z., Dan, Z., Li-na, W. et al. Synthesis, characterization and properties of LiFePO4/C cathode material. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 10, 909–912 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02832437
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02832437