Abstract
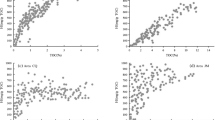
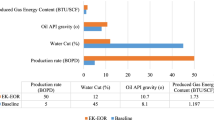
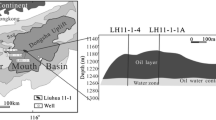
Geochemical methods can be used to optimize heavy oil reservoir management. The distribution of some biomarkers in oils is different with the degree of biodegradation. Geochemical parameters can be used to predict oil viscosity and thus to preliminarily evaluate the difficulties involved in oil production. The results of viscosity prediction for oils from reservoir S 23 in block Leng 43 and preliminary evaluation of oil production difficulty are consistent with the geological data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baskin, D. K., R. J. Hwang, and R. K. Purday, 1995, Predicting gas, oil, and water intervals in Niger delta reservoirs using gas chromatography [J]: AAPG, v. 79, n. 3, p. 337–350.
Hong Shiduo, 1985, Reservoir physics [M]: Beijing, Petroleum Industry Press, 168p.
Hou Dujie, Zhang Min, Zhao Hongjing, and Chen Qi, 2001, Introduction to reservoir and production geochemistry [M]: Beijing, Petroleum Industry Press, 260p.
Karlsen, D. A. and S. Larter, 1991, Analysis of petroleum fractions by TLC-FID: applications to petroleum reservoir description [J]: Organic Geochemistry, v. 17, p. 603–617.
Kaufman, R. L. and A. S. Ahmed, 1990, Gas chromatography as a development and production tool for fingerprinting oils from individual reservoirs: application in the Gulf of Mexico [J]: Gulf Coast Section of the Society of Economic Paleontogists and Mineralogists Foundation Ninth Annual Research Conference Proceedings, p. 263–282.
Larter, S. R. and A. C. Aplin, 1995, Reservoir geochemistry: methods, applications and opportunities, in J. M. Cubitt and W. A. England, eds., The geochemistry of Reservoirs [M]: Geological Society Special Publication, p. 5–32.
McCaffrey, M. A., H. A. Legrre, and S. J. Johnson, 1996, Using biomarkers to improve heavy oil reservoir management: an example from the Cymric Field, Kem County, California [J]: AAPG, v. 80, n. 6, p. 898–913.
Peters, K. E. and J. M. Moldwan, 1993, The biomarker guide: interpreting molecular fossils in petroleum and ancient sediments: Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey [M]: Prentice Hall, 360p.
Slentz, L. W., 1981, Geochemistry of reservoir fluids as a unique approach to optimum reservoir management [C]: Society of Petroleum Engineers paper 9582, Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineer Middle East Technique Conference, Manama, Bahrain, p. 37–50.
Tissot, B. P. and D. H. Welte, 1984, Petroleum formation and occurrence (2nd edit.) [M]: Springer Verlag, Berlin, 699p.
Zhao Hongjing, Zhang Min, Zhang Chunming, and Mei Bowen, 2002, Viscosity predicting of biodegraded oils on aromatic compounds [J]: Acta Sedimentologica Sinica (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hongjing, Z., Chunming, Z., Bowen, M. et al. New technology of optimizing heavy oil reservoir management by geochemical means: A case study in block Leng 43, Liaohe Oilfield, China. Chin. J. Geochem. 21, 340–347 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02831535
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02831535