Abstract
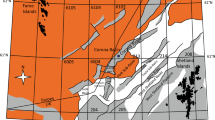
In the Tuoshi oilfield, located in the Cenozoic Jianghan Basin of southeastern China, there have been found hydrocarbon reservoirs hosted in lacustrine sandstones of the Eogene Xingouzui Formation. The main diagenetic features identified in these sandstones include the dissolution of detrital K-feldspar and albite grains, the precipitation of quartz as overgrowths and/or cements, and the precipitation and/or transformation of clay minerals. These diagenetic features were interpreted to have occurred in early, intermediate and late stages, based on the burial depth.
The kinetics of fluid-mineral reactions and the concentrations of aqueous species at each stage of diagenesis were simulated numerically for these lacustrine sandstones, using a quasi-stationary state approximation that incorporates simultaneous chemical reactions in a time-space continuum. During the early diagenetic stage, pore fluid was weakly acidic, which resulted in dissolution of K-feldspar and albite and, therefore, led to the release of K+, Na+, Al3+ and SiO2(aq) into the diagenetic fluid. The increased K+, Na+, Al3+ and SiO2(aq) concentrations in the diagenetic fluid caused the precipitation of quartz, kaolinite and illite. At the beginning of the intermediate diagenetic stage the concentration of H+ was built up due to the decomposition of organic matter, which was responsible for further dissolution of K-feldspar and albite and precipitation of quartz, kaolinite, and illite. During the late diagenetic stage, the pore fluid was weakly alkaline, K-feldspar became stable and was precipitated with quartz and clay minerals. When the burial depth was greater than 3000 m, the pore fluids became supersaturated with respect to albite, but undersaturated with respect to quartz, resulting in the precipitation of albite and the dissolution of quartz.
The diagenetic reactions forecasted in the numerical modeling closely matched the diagenetic features identified by petrographic examination, and therefore, can help us to gain a better understanding of the diagenetic processes and associated porosity evolution in sandstone reservoirs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Helgeson, H. C., 1968, Evaluation of irreversible reactions in geochemical processes involving minerals and aqueous solutions II, Application [J]: Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, v. 32, p. 853–877.
Helgeson, H. C. and W. M. Murphy, 1983, Calculation of mass transfer among minerals and aqueous solution as a function of time and surface area in geochemical processes I, Computational approach [J]: Journal of the International Association for Mathematical Geology, v. 15, p. 109–130.
Helgeson, H. C., W. M. Murphy, and P. Aagaard, 1984, Thermodynamic and kinetic constraints on reaction rates among minerals and aqueous solution 2: Rate constants, effective surface area, and the hydrolysis of feldspar [J]: Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, v. 48, p. 2405–2432.
Lichtner, P. C., 1993, Scalling properties of time-space kinetic mass transport equations and the local equilibrium limit [J]: American Journal of Science, v. 293, p. 257–296.
Lichtner, P. C., 1992, Time-space continuum description of fluid/rock interaction in permeable media [J]: Water Resources Research, v. 28, p. 3135–3155.
Lichtner, P. C., 1988, The quasi-stationary state approximation to coupled mass transport and fluid-rock interaction in a porous medium [J]: Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, v. 52, p. 143–165.
Lichtner, P. C., 1985, Continuum model for simultaneous chemical reactions and mass transport in hydrothermal systems [J]: Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, v. 49, p. 779–800.
Lichtner, P. C. and G. G. Biino, 1992, A first principles approach to supergene enrichment of a porphyry copper protore I, Cu-Fe-S-H2O subsystem [J]: Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, v. 56, p. 3987–4013.
Lichtner, P. C. and N. Waber, 1992, Redox front geochemistry and weathering: Theory with application to the Osamu Utsumi uranium mine, Pocos de Caldas, Brazil [J]: Journal Geochemical Exploration, v. 45, p. 521–564.
Liu Lihua, Ni Shijun, Luo Yutian, and Wang Xuben, 1992, Diagenesis of the sandstone in the lower member of Eogene Xingouzui Formation in Tuoshi oil field, Hubei Province [J]: Petroleum Exploration and Development, v. 5, p. 18–24 (in Chinese).
Murphy, W. M. and H. C. Helgeson, 1989, Thermodynamic and kinetic constraints on reaction rates among minerals and aqueous solution 4: Retrieval of rate constant and activation parameters for the hydrolysis of pyroxene, wollastonite, olivine, andalusite, quartz, and nepheline [J]: American Journal of Science, v. 289, p. 17–101.
Ni Shijun, Luo Yutian, Liu Lihua, Wang Xuben, Li Sue, Luo Yangdi, and Han Dingrong, 1994, Thermodynamics of diagenetic fluid and fluid/mineral reactions in the Eogene Xingouzui Formation, oil field T, Jianghan basin [J]: Chinese Journal of GEOCHEMISTRY, v. 13, p. 193–201.
Ni Shijun, Yang Weidong, Tang Jianwu, Jin Jinfu, Wang Xuben, Liu Li, Luo Yutian, Liu Lihua, Li Sue, and He Qichuan, 1996, Geochemical behavior of the reactive elements during burial diagenesis of sediment [M]: Chengdu, Sichuan Publishing House of Science & Technology,p. 1–82 (in Chinese).
Steefel, C. I. and P. V. Cappellen, 1990, A new kinetic approach to modeling water-rock interaction; The role of nucleation, precursors, and Ostwald ripening [J]: Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, v. 54, p. 2657–2677.
Tang Jianwu, Ni Shijun, and Wang Xuben, 1996, A numerical calculation program of geochemical kinetics to diagenetic fluid-mineral intereaction [J]: Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, v. 18, p. 287–293 (in Chinese).
Wang Xuben, Ni Shijun, Luo Yutian, Yang Saoguo, and Liu Lihua, 1996, Geothermal evolution characteristics and their geological interpretation of the Tuoshi area in Jianghan basin [J]: Journal of Chengdu Institute of Technology, v. 23, p. 30–35 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This project was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 49133080), and by the Trans-century Training Programme Foudation for the Talents sponsored by the State Education Commission of China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shijun, N., Hairuo, Q., Jianwu, T. et al. Kinetic modeling of diagenesis of Eogene lacustrine sandstone reservoirs in the Jianghan Basin, southeastern China. Chin. J. Geochem. 21, 298–307 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02831531
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02831531