Abstract
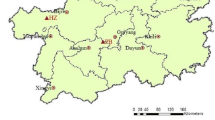
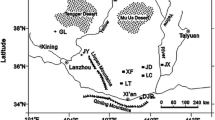
Organic carbon isotopic composition (δ13C ) is one of the important proxies in paleoenvironment studies. In this paper modern plant δ13C in the arid areas of China and Tibetan Plateau is studied. It is found that most terrestrial plant species in western China are C3 plants with δ13C values ranging from -32.6‰ to -23.2‰ and only few species are C4 plants with δ13C values from -16. 8‰ to -13.3‰ The δ13C is closely related to precipitation (or humidity), i. e., light δ13C is related to high precipitation (or humid climate), while heavy δ13C to low precipitation (or dry climate), but there is almost no relation between plant δ13C and temperature. Submerged plants have δ13C values ranging from -22.0‰ to -12.7‰, like C4 plants, while merged plants have δ13C values ranging from -28. 1‰ to -24. 5‰, like C3 plants. It can then be concluded that organic δ13C variations in terrestrial sediments such as loess and soil in western China can indicate precipitation changes, but those in lake sediments can reflect organic sources and the productivity of different types of aquatic plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aravena, R., B. G. Warne, G. M. MacDonald, and K. I. Hanf, 1992, Carbon isotope composition of lake sediments in relation to lake productivity and radiocarbon dating [J]: Quaternary Research, v. 37, p. 333–345.
Bird, M.I., A. R. Chivas, and J. A. Head, 1996, Latitudinal gradient in carbon turnover times in forest soils [J]: Nature, v. 381, p. 143–146.
Davidson, G. R., 1995, The stable isotopic composition and measurement of carbon in soil CO2 [J]: Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, v. 59, p. 2485–2489.
Edwards, T. W. D., W. Graf, P. Trimborn, W. Stichler, J. Iipp, and H. D. Payer, 2000, δ13C response surface resolves humidity and temperature signals in tree stem cellulose of bean plants (Vicia faba) [J]: Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, v. 64, n. 2, p. 161–167.
Frakes, L. A. and Sun Jianzhong, 1994, A carbon isotope record of the upper Chinese loess sequence; estimates of plant types during stadials and interstadials [J]. Palaeos, v. 108, p. 183–189.
Friend, A.D., F.I. Woodward, and V. R. Switsaur, 1989, Field measurements of photosynthesis, stomatal conductance, leaf nitrogen and δ13 C along altitudinal gradients in Scotland [J]: Funtional Ecology, v. 3, p. 117–122.
Guillet, B, P. Faivre, A. Mariotti, and J. Khobzi, 1988, The14C dates and13C/12C ratios of soil organic matter as a means of studying the past vegetation in intertropical regions; examples from Columbia (South America) [J]; Palaeos., v. 65, p. 51–58.
Hatte, C., M. Fontugne, D. D Rousseau, P. Antoine, L. Zöller, N. Tisnérat-Laborde, and L. Bentaleb, 1998, δ13C variations of loess organic matter as a record of the vegetation response to climatic changes during the Weichselian [J]: Geology, v. 26, n. 7, p. 583–586.
Krishnamurthy, R. V. and M. DeNiro, 1982, Isotope evidence for Pleistocene climate changes in Kashmir, India [J]: Nature, v. 298, p. 640–641.
Lin Ruifen and Wei Keqin, 2000, A δ13C record of the organic matter in lacustrine sediments of the core ZHJ from lake Caohai and its palaeoclimate implications [J]; Geochimica, v. 29, n. 4, p. 390–396 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Luo Yaohua, 1985, The ecological significance of C3, C4 and CAM photosynthesis path [J]; Ecologica Acta, v. 5, n. 1, p. 15–27 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Oana, S. and E. S. Deevey, 1960, Carbon 13 in lake waters and its possible bearing on paleolimnology [J]; American Journal of Science,. 258(A), p. 253–272.
Wang Hong and L. R. Follmer, 1998, Proxy of monsoon seasonality in carbon isotopes from paleosols of the southern China Loess Plateau [J]: Geology, v. 26, n. 11, p. 987–990.
Wu Jinglu and Wang Suming, 1996, Climate versus changes in δ13 C values of the organic matter in lake sediments [J]: Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, v. 16, n. 2, p. 103–109 (in Chinese).
Zhang Chengjun, Chen Fahu, and Sun Weizhang, 2000, The Paleoenvironmental significance of δ13Corg in Jiuzhoutai S0 Paleosol, In: Thesis Volume of the Chinese Post-Doctoral Congress in 2000, Nanjing [D]: Beijing, Science Press, p. 85–89 (in Chinese).
Zhang Chengjun, Chen Fahu, Shi Qi, Sun Weizheng, and Tang Furong, 2000, Carbon isotopic record of lake organic matter during Holocene climatic variations in the arid-semiarid areas of Northwest China-Taking Sanjiaocheng in the drainage area of the Shiyang River as an example [J]: Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, v. 20, n. 4, p. 93–97 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Chengjun, Chen Fahu, Wang Qi, Shi Qi, and Sun Weizheng, 2000, Unstablity record of late glacial period in the Shiyang River Basin of arid northern China [J]: Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, v. 18, n. 6, p. 646–650 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Pingzhong, Wang Xiangbing, Chen Jiangfa, and Wang Suming, 1995, A lake fluctuation evaluation proxy-hydrogen index and carbon isotopic composition of lake organic matter; example from core RH [J]; Chinese Science Bulletin, v. 40, n. 18, p. 1682–1685 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Granted by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 40041004 and G1999043501 ).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chengjun, Z., Fahu, C. & Ming, J. Study on modern plant C-13 in western China and its significance. Chin. J. Geochem. 22, 97–106 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02831518
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02831518