Abstract
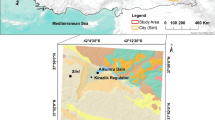
Based on field survey located by GPS, it is obtained landslides' location and distribution information by the method of remote sensing in this paper. The vector data of environmental factors that breed and induce landslides such as the elevation, the slope, the vegetation cover, the lithology, the rainfall and so on are gained using GIS (geographical information system) techniques of spatial analysis. All the data obtained are managed through building landslide management system. At the same time, the system is made the platform to appraise the relationship between the distribution of landslides and the environmental factors. The results indicate: landslides take place relatively easily in the slope range between 10° and 25°; most landslides are in the mixed area of bush and grass with a coverage degree of from 20% to 65%; the distribution of landslides has a positive relationship with the distribution of annual rainfall. The risk degree of Panxi Area is zoned and mapped by the model of liner stack using GIS technique, and the result indicates: the place of high risk degree is the belt of Panzhihua-Miyi-Dechang-Mugu and southeast of Huili county and Huidong county, and area is about 512 707 hm2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Su Chunjiang, Xu Yun, Fang Yiping. Bio-Resource Exploitation and Ecological and Environmental Construction-Taking Panxi Area as an Example [J].Journal of Mountain Science (Suppl), 2004,22: 143–148 (Ch).
Ran Ruiping. Countermeasures to Eco-Environmental Problems in Panxi Area [J].Journal of Mianyang Normal University, 2004,23(5): 77–81 (Ch).
Li Houqiang, Ding Jin, Ai Nanshan, Theoretical Studies on the Panxi Region Landslide Development [J].The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1997,8(1): 12–16 (Ch).
Ji Yutian. Analysis and Forecast on the Relationship between Landslides and Debrio-Flows in Panxi Region [J].Journal of Sichuan Meteorology, 1999,19(3), 34–38 (Ch).
Eyers R, Moore J, Hervas, J,et al. Geohazards in Engineering Geology [M]. London: Geological Society Special Publication, 1998: 133–140.
Zhang Renhua.Experimental Remote Sensing Model and Groundwork [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1994: 104–113 (Ch).
Donati L, Turrini M. An Objective Method to Rank the Importance of Factors Predisposing to Landslides with the GIS Methodology: Application to an Area of the Apennines (Valneria; Perugia, Italy) [J].Eng Geol, 2002,63: 277–289.
Liu Chuanzheng, Li Tiefeng, Wen Mingsheng,et al. Assessment and Early Warning on Geohazard in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region of Changjiang River [J].Hydrography and Engineering Geology, 2004,4: 4–19 (Ch).
Chung C H, Fabbri A, Van Westen C. Multivariate Regression Analysis for Landslide Hazard Zonation [C]//Carrara A, Guzzetti F. Geographical Information Systems in Assessing Natural Hazards, Netherland: Kluwer Academic Publisher, 1995: 107–133.
Qiao Jianping, Zhao Yu, Yang Wen. Study on Landslide Danger Degree Division in the Area of Sichuan Province and Chongqing City [J].Journal of Natural Disasters, 2000,9 (1): 68–71 (Ch).
Carrara A, Cardinali M, Detti R,et al. GIS Techniques and Statistical Models in Evaluating Landslide Hazard [J].Earth Surf Proc Land, 1991,12: 427–445.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Supported by the Knowledge Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX2-SW-319-01) and the Project of Science and Technology Bureau of Sichuan Province ([2005]-172-140107)
Biography: ZHANG Baolei (1979-), male, Ph. D. candidate, research direction: application of RS and the development of GIS.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baolei, Z., Shujun, S., Wenlan, F. et al. Assessment and risk zonation of landslides in Panxi Area based on 3S Technology. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 11, 793–800 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02830166
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02830166