Summary
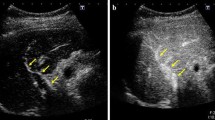
The focal hepatic lesion caused by local injection of absolute alcohol in rats was evaluated with ultrasonic contrast agent and pathologic examination. Twenty adult Wistar rats weighing about 200 g were injected with absolute alcohol (0.05–0.1 mL each one) on the exterior left lobe of the liver under the monitoring of ultrasound. Pulse inversion harmonic imaging was used to evaluate the focal lesion after bolus injection of ultrasonic contrast agent (0.05 mL/200 g) through caudal vein. Seven days later, the focal lesion was studied again as before. The exterior left lobe of liver with focal lesion was incised and underwent pathologic examination. The results showed that all of the focal lesions could be defined clearly after bolus injection of the ultrasonic contrast agent under the mode of pulse inversion harmonic imaging. There was good correlation between the size of the focal lesion measured by ultrasound on the 7th day after the “ablation” under the mode of pulse inversion harmonic imaging and that gotten by pathologic examination (P=0.39). The focus size measured by ultrasound right after the ablation was larger than that gotten by pathologic examination (P=0.002). It was concluded that ultrasonic contrast agent plus pulse inversion harmonic imaging could be used to assess the size of the focal hepatic lesion caused by local injection of absolute alcohol in rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rabenandrasana H A, Furukawa A, Furuichi Ket al. Comparison between tissue harmonic imaging and liver-specific late-phase contrast-enhanced pulse-inversion imaging in the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver metastasis. Radiat Med, 2004, 22(2): 90–97
Meloni M F, Goldberg S N, Livraghi Tet al. Hepatocellular carcinoma treated with radio frequency ablation: comparison of pulse inversion contrast enhanced harmonic sonography, contrast enhanced power Doppler sonography, and helical CT. AJR, 2001, 177(2): 375–380
Buscarini L, Buscarini E, Distasi Met al. Percutaneous radio frequency thermal ablation combined with transcatheter arterial embolization in the treatment of large hepatocellulor carcinoma. Ultraschall Med, 1999, 20: 47–53
Chen X M, Lin H H, Luo P Fet al. Pathological study of resected specimens of hepatocellular carcinoma after different ways of interventional treatment. Chin J Radiol (Chinese), 2001, 35(12): 903–907
Yang Y H, Lin L W, Yang F Det al. The experimental pathological study of transplantable human hepatocellular carcinoma model in node mice treated with Chinese medicine “99-star” by ultrasound guide percutaneous injection. Fu Jian Yi Yao Za Zhi (Chinese), 2002, 2(1): 74–75
Ballad E M, Vezirov S Y, Pfleiderer Ket al. Nonlinear modulation technique for NDE with air-coupled ultrasound. Ultrasonics, 2004, 42(1–9): 1031–1036
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
ZHANG Chao, male, born in 1976, Attending Physician
This project was supported by a grant from Hubei Provincial Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 2004ABA247).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chao, Z., Youbin, D., Daozhong, H. et al. Dynamic assessment of the focal hepatic lesion in rats using ultrasonic contrast agent. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 26, 332–333 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02829567
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02829567