Summary
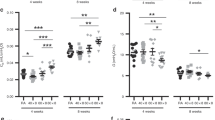
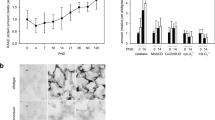
To investigate whether treatment with retinoic acid (RA) could improve level of lung alveolarization and influence lung collagen in newborn rats exposed to hyperoxia, newborn Sprague-Dawley rats aged 2 days were randomly assigned to 8 groups: (1) air, (2) O2, (3) air+NS, (4) O2+NS, (5) air+dex, (6) O2+dex, (7) air+RA and (8) O2+RA. Group 2, 4 6 and 8 were kept in chambers containing 85% oxygen, the values were checked 3 times a day. The other 4 groups were exposed to room air. Level of alveolarization and lung collagen were analyzed at age of 14 or 21 days through radial alveolar counts, alveolar airspace measurements, type I, II collagen immunohistochemical methods (SP method) and image processing system. Transforming growth factor-β receptors and procollagen mRNA accumulation were examined at age of 14 days through immunohistochemical methods andin situ hybridization. Our results showed that radial alveolar counts were increased and distal airspace was enlarged in group 8. Type I collagen was markedly increased, and transforming growth factor-β receptors and procollagen mRNA were decreased by retinoic acid in bronchial epithelial cells, alveolar epithelial cells and alveolar intersitium. It is concluded that retinoic acid can partially reverse lung development arrest during exposure to hyperoxia by increasing lung collagen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cherif A, Marrakchi Z, Chaouachi Set al. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia and corticosteroid therapy. Arch Pediatr, 2002, 9(2): 159
Veness-Meehan K A, Bottone F G Jr, Stiles A D. Effects of retinoic acid on airspace development and lung collagen in hyperoxia-exposed newborn rats. Pediatr Res 2000, 48 (4): 434
Massaro G D, Massaro D Postnatal treatment with retinoic acid increases the number of pulmonary alveoli in rats. Am J Physiol, 1996, 270 (2 Pt 1): L305
Jakkula M, Le Cras T D, Gebb Set al. Inhibition of angiogenesis decreases alveolarization in the developing rat lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2000, 279 (3): L600
Hayashi T, Stetler-Stevenson W G, Fleming M Vet al. Immunohistochemical study of metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in the lungs of patients with diffuse alveolar damage and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol, 1996, 149 (4): 1241
Massaro D, Teich N, Massaro G D Postnatal development of pulmonary alveoli: modulation in rats by thyroid hormones. Am J Physiol, 1986, 250 (1 Pt 2): R51
Fraslon C, Bourbon J R. Retinoids control surfactant phospholipid biosynthesis in fetal rat lung. Am J Physiol, 1994, 266 (6 Pt 1): L705
Chytil, F. Retinoids in lung development. FASEB J, 1996, 10: 986
Eickelberg O, Kohler E, Reichenberger Fet al. Extracellular matrix deposition by primary human lung fibroblasts in response to TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta 3. Am J Physiol, 1999, 276 (5 Pt 1): L814
Pardo A, Barrios R, Maldonado Vet al. Gelatinases A and B are up-regulated in rat lungs by subacute hyperoxia: pathogenetic implications. Am J Pathol, 1998, 153 (3): 833
Frankenberger M, Hauck R W, Frankenberger Bet al. All trans-retinoic acid selectively down-regulates matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and up-regulates tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) in human bronchoalveolar lavage cells. Mol Med, 2001, 7(4): 263
Nabeyrat E, Corroyer S, Besnard Vet al. Retinoic acid protects against hyperoxia-mediated cell-cycle arrest of lung alveolar epithelial cells by preserving late G1 cyclin activities. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2001, 25(4): 507
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
CHANG Liwen, female, born in 1948, Professor
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liwen, C., Zhihui, R., Qianshen, Z. et al. Effect of retinoic acid on lung injury in hyperoxia-exposed newborn rats. Current Medical Science 23, 71–74 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02829469
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02829469