Summary
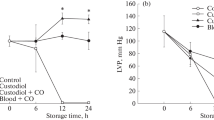
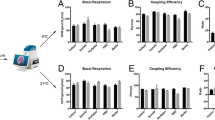
The cardioprotective effects of melatonin on recovery of rat donor hearts after 12 h of preservation were investigated. Wistar rats weighing 200 to 250 g (n=24) were randomly divided into 3 groups. In the non-storage group (n=8), donor hearts were not stored. In the melatonin group (n=8), donor hearts were stored in 4°C St. Thomas solution with melatonin (0.1 mmol/L). In the control group (n=8), donor hearts were stored in 4°C St. Thomas solution only. The coronary flow (CF), cardiac function, coronary vasodilatory response, creatine kinase (CK) and high energy phosphate levels were measured after the hearts had been preserved for 12 h. Transmission electron microscopy was used to examine the microstructural changes after 12 h of preservation. The recovery of cardiac function and coronary vasodilatory response were significantly improved in the melatonin group (P<0.01). CK release decreased greatly in the melatonin group (P<0.01). High energy phosphate levels were significantly better preserved in the melatonin group (P<0.01). Histological findings were much better in the melatonin group than in the control group. These results suggest that melatonin has cardioprotective effects on the recovery of rat donor hearts after 12 h of preservation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hauptman P J, Aranki S, Mudge G H Jret al. Early cardiac allograft failure after orthotopic heart transplantation. Am Heart J, 1994, 127:179
Beyer C E, Steketee J D, Saphier D. Antioxidant properties of melatonin—An emerging mystery. Biochem Pharmacol, 1998, 56(10):1265
Kaneko S, Okumura K, Numaguchi Yet al. Melatonin scavenges hydroxyl radical and protects isolated rat hearts from ischemic reperfusion injury. Life Sci, 2000, 67(2):101
Dhalla NS, Elmoselhi AB, Hata Tet al. Status of myocardial antioxidants in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res, 2000, 47:446
Suzuki Y J, Forman H J, Sevanian A. Oxidants as stimulators of signal transduction. Free Radic Biol Med, 1997, 22:269
Zemkova H, Vanecek J. Differences in gonadotropin-releasiug hormone-induced calcium signaling between melatonin-sensitive and melatonin-insenstive neonatal rat gonadotrophs. Endocrinology, 2000, 141(3):1017
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
GAO Sihai, male, born in 1973, Doctor in Charge
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sihai, G., Ping, L., Tiecheng, P. et al. Cardioprotective effects of melatonin on recovery of rat donor hearts after 12-hour preservation. Current Medical Science 23, 407–410 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02829430
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02829430