Abstract
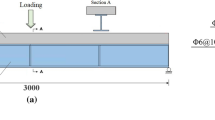
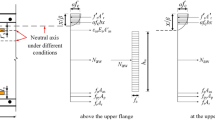
This paper presents the behavior characteristics of steel-concrete interface and analysis method to simulate interface behavior by using push-out results for steel-concrete composite members. In order to analyze the partial-interaction behavior of steel-conc rete interface, the interface is idealized by a number of interface elements. A total of 9 push-out specimens were tested and the test results were utilized to provide the properties of interface element in the analysis. To validate the present study, using a commercial structural analysis program, nonlinear structural analysis were performed for the push-out specimens, and the results of analysis were compared with the test data. The results of this study have shown that the nonlinear, slip-softening, as well as linear-elastic behaviors of steel-concrete interface can be efficiently and accurately simulated by the method of analysis presented in this paper.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frits, C.W. and Peter, H.F. (1998).DIANA User's manual: nonlinear analysis-release 7, TNO.
Ivan, M.V., Joseph, P.C., Richard, W.F., Lawrence, G.G., Roberto, T.L., and Loring, A.W. (1997).Composite construction design for Buildings, McGraw-Hill.
Jeong, Y.J. and Jung, K.H. (2002). “Nonlinear analysis with slip in steel-concrete composite structures.” (in Korean)J. of the Korean Society of Civil Engineering, Vol. 22, No. 1-A, pp. 31–42.
Johnson, R.P. (1994).Composite structures of steel and concrete, Blackwell Scientific Publications.
Oehlers, D.J. and Johnson, R.P. (1987). “The strength of stud shear connections in composite beam.”The Structural Engineer, Vol. 65B, No. 2, pp. 44–48.
Oehlers, D.J. and Bradford, M.A. (1999).Elementary behavior of composite steel & concrete structural members, Butterworth-Heinemann.
Oehlers, D.J., Seracino, R., and Yeo, M.F. (2000). “Fatigue behavior of composite steel and concrete beams with stud shear connections.”Prog. Struct. Engng. Mater., pp. 187–195.
Salari, M.R. and Spacone, E. (2001). “Finite element formulations of one-dimensional elements with bond-slip.”Engineering Structures, Vol. 23, pp. 815–826.
Soh, C.K., Chiew, S.P., and Dong, Y.X. (1999). “Damage model for steel-concrete interface.”J. of Engineering Mechanics, Vol. 125, No. 8, pp. 979–983.
Soh, C.K., Chiew, S.P., and Dong, Y.X. (2002). “Concrete-steel bond under repeated loading.”Magazine of Concrete Research, Vol. 54, No. 1, pp. 35–46.
Veljkovic, M. (1996).Behavior and resistance of composite slabs, Ph.D. Dissertation, Lulea University, Sweden.
Veljkovic, M. (2001).Behavior of shear studs under repeated load, Lulea University, Sweden.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, Y.J., Kim, H.Y., Koo, H.B. et al. Steel-concrete interface behavior and analysis for push-out. KSCE J Civ Eng 9, 119–124 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02829065
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02829065