Summary
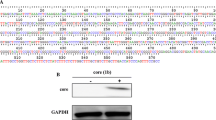
In order to investigate the effect of small ubiquitin-like modifier-1 (SUMO-1) on the p53-induced HepG2 cell apoptosis, HepG2 cells were transfected by recombinant plasmids as pwtp53, pMDM2 and pSUMO-1 respectively. Western blot was employed to detect the protein expression of the transfected recombinant plasmids and the rate of apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry. The results showed that in cells transfected with pwtp53 and pwtp53+pSUMO-1, the apoptosis rate was (16.79±1.62)% and (18.15±1.36)% respectively, while transfected with pwtp53+pMDM2, the rate was decreased to (5.17±1.23)%. The apoptosis rate was (14.06±1.84)% in the cells transfected with pwtp53+pMDM2+pSUMO-1, significantly higher than that in the cells Transfected with pwtp53+pMDM2 (P<0.01). The apoptosis rates in the cells were all less than 2% and had no significant difference among the groups. It was suggested that in the HepG2 cells, SUMO-1 can increase the apoptosis induced by wild-type p53 through binding to p53 protein, posttranslational modification and inhibiting the p53 degradation by MDM2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ko L J, Prives C. p53: puzzle and paradigm. Genes Dev, 1996,10(9):1054
Rosenfeld M R, Meneses P, Dalmau Jet al. Gene transfer of wild-type p53 results in restoration of tumor-suppressor function in a medulloblastoma cell line. Neurology, 1995, 45(8):1533
Honda R, Tanaka H, Yasuda H. Oncoprotein MDM2 is a ubiquitin ligase E3 for tumor suppressor p53. FEBS Lett, 1997,420(1):25
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz Aet al. Mdm2 promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature, 1997,387(6630): 296
Saitoh H, Hinchey J Functional heterogeneity of small ubiquitin-related protein modifiers SUMO-1 versus SUMO-2/3. J Biol Chem, 2000,275(9):6252
Muller S, Hoege C, Pyrowolakis Get al. SUMO, ubiquitin’s mysterious cousin. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2001,2(3):202
Melchior F. SUMO-nonclassical ubiquitin. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol, 2000,16:591
Rodriguez M S, Desterro J M, Lain Set al. SUMO-1 modification activates the transcriptional response of p53. Embo J, 1999,18(22):6455
Sambrook J, Ftitsch E, Mauitis T. Molecular cloning. 2nd ed. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1988, 362–371, 792–793
Zheleva D I, Lane D P, Fischer P M. The p53-Mdm2 pathway: targets for the development of new anticancer therapeutics. Mini Rev Med Chem, 2003,3(3):257
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Lu Xingrong, male, born in 1970, Doctor in Chargo M. D., Ph. D.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xingrong, L., Jilin, Y. SUMO-1 enhancing the p53-induced HepG2 cell apoptosis. Current Medical Science 25, 289–291 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02828145
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02828145