Abstract
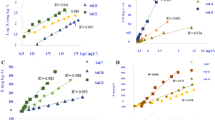
pH of soil pore water is the important factor in heavy metal retention and migration in soil. Buffer capacity of clays such as kaolinite, hectorite, attapulgite, and Na-bentonite were determined. The magnitude of buffer capacity is in the order of hectorite>Na-bentonite>attapulgite>kaolinite. Carbonate content and CEC of soil affect most on the magnitude of buffer capacity while effects of organic content and surface area were negligible. Attempts were made to simulate buffer capacity experimental results in this research. In order to model the buffer capacity of soil, chemical interactions between proton and surface functional group were modeled using the diffuse double layer theory. An empirical model as functions of carbonate content and CEC were proposed as well. Predictions made by the diffuse double layer model agreed with experimental results well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cang, D, Wang, J., and Zhang, X. (1985). “Acidity.”Physical chemistry of paddy soils, Science Press, Beijing, China, pp. 131–156.
Curtin, D., Campbell, C. A., and Messer, D. (1996). “Prediction of titrable acidity and soil sensitivity to pH change.”J. Environ. Qual. ASA, 25(6), pp. 1280–1284.
Dowdy, R. H., and Volk, V. V. (1983). “Movement of heavy metals in soils.”Proceedings of American Society of Agronomy and the Soil Science Society of America, Atlanta, Georgia, 29 Nov.3 Dec. 1981, pp. 229–239.
Dzombak, D. A., and Morel, F. M. M. (1990).Surface complexation modeling. John Wiley & Sons, New York, N.Y.
Eltantaway, I. N. and Arnold, P. W. (1973). “Reappraisal of ethylene glycol mono-ethyl ether (EGME) method for surface area estimation of clays.”Soil Sci. Vol. 24, pp. 232–238.
Harter, R. D. (1983). “Effect of soil pH and adsorption of lead, copper, zinc, and nickel.”Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., Vol. 47. pp. 47–51.
Loeppert, R. H. and Suarez, D. L. (1996). “Carbonate and Gypsum.”Method of Soil Analysis: 3. Chemical Analysis., Soil Science Society of America, pp. 437–474.
McBride, M. M. (1994).Environmental chemistry of soils. Oxford University press, New York, Oxford.
Mitchell, J. K. (1993).Fundamentals of Soil Behavior., John Wiley and Sons, Inc. New York.
Singh, U., and Uehara, G. (1986). “Electrochemistry of the double-layer: Principles and applications to soils.”Soil physical chemistry, Sparks, D. L., ed., CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp. 1–38.
Stumm, W., and Morgan, J. J. (1996).Aquatic chemistry. 3rd Ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY.
Summer, M. E., Miller, W. P. (1996). “Cation exchange capacity and exchange coefficients.”Method of Soil Analysis: 3. Chemical Analysis., Soil Science Society of America, pp. 1201–1229.
Soil Analysis: 3. Chemical Analysis., Soil Science Society of America, pp. 1011–1069.
Thomas, G. W. (1996). “Soil pH and soil acidity.”Method of Soil Analysis: 3. Chemical Analysis., Soil Science Society of America, pp. 475–490.
Van Breeman and Wielemaker, W. G. (1974). “Buffer intensities and equilibrium pH of minerals and soils, II. Theoretical and actual pH of minerals and soils.”Soil, Sci. Soc. Proc. Vol. 38, pp. 61–66.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The manuscript for this paper was submitted for review on October 9, 2000.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, G. Influence of physicochemical properties of soil on pH of pore water. KSCE J Civ Eng 4, 233–237 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02823971
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02823971