Abstract
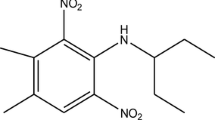
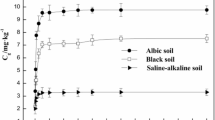
The purpose of this study is to elucidate the adsorption, desorption and movement of napropamide in soils, that have been mainly used in farmland. Experiments were carried out with the adsorption and desorption tests on various shaking time, temperature, pH and the content of organic matter, and column test, in order to understand the movement characteristics of napropamide. As results, the isothermal adsorption characteristics of napropamide were well fitted with the Freundlich rather than with the Langmuir equation. When the content of organic matter in soil exceeded 2.0%, the adsorption rate of napropamide depended on the content of organic matter. However, in case the content of organic matter was below 2.0%, the content of clay became a determiner. Adsorption and desorption was little affected by pH. Though the adsorption was affected by soil temperature, desorption was little. The slope of adsorption curve was in the order of sandy loam>loam>silty clay. But a lot of napropamide was desorbed from the silty clay soil, even though its movement was slower than other two soils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, G.W. and White, J.L. (1970). “Factors influencing the adsorption, desorption and movement of pesticides in soil.”Residue Review, Vol. 32, pp. 29–92.
Bowman, B.T. and Sans, W.W. (1985). “Partitioning behavior of insecticides in soil-water systems: II. Desorption hysteresis effects.”J. Environ. Qual., Vol. 14, pp. 270–273.
Chiou, C.T., Malcolm, R.L., Brinton, T.I., and Kile, D.E. (1986). “Water solubility enhancement of some organic pollutants and pesticides by dissolved humic and fulvic acids.”Environ. Sci. Technol., Vol. 20, pp. 502–508.
Cho, I.H. (1997). “Adsorption Characteristics of Benzene, Phenol and A Mixture (Benzene+Phenol) on XAD-4 and Coal Char.”Environ. Eng. Res., Korean Society of Environmental Engineers, Vol. 2, No. 3, pp. 201–205.
Gerstl, Z. and Yaron, B. (1983). “Behavior of bromacil and napropamide in soils: I. Adsorption and degradation.”Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., Vol. 47, pp. 474–478.
Ghosh, K. and Schnitzer, M. (1980). “Macromolecular structures of humic substances.”Soil Sci., Vol. 129, pp. 266–278.
Han, S.S., Jeong, J.H., and Choi, C.G. (1994). “Resideue of Herbicide Napropamide and Change of Microorganism in Upland Soil Under Different Environmental Conditions.”Kor. J. Weed Sci., Vol. 14, No. 4, pp. 298–313.
Hata Y. and Nunoshige, T. (1982). “Adsorption and desorption of piperophos by soil.”J. Pesticides Sci., Vol. 7, p. 155.
Hu, W., Lee, S.J., and Kim, J.E. (1997). “Adsorption-desorption, leaching, and degradation pattern of fungicide fluazinam in the soil environment.”Agricultural Chemistry and Biotechnology, Vol. 40, No. 2, pp. 128–133.
Huang, P.M., Grover, R., and Mckercher, R.B. (1984). “Components and particle size fractions involved in atrazine adsorption by soils.”Soil Sci., Vol. 138, pp. 20–24.
Kim, C.G. (2002). “Adsorption Behaviour of Thiophene Derivatives on Soil Materials.”Environ. Eng. Res., Korean Society of Environmental Engineers, Vol. 7, No. 4, pp., 207–217.
McGlamery, M.D. and Slife, F.W. (1966). “The adsorption and desorption of atrazine as affected by pH, temperature, and concentration.”Weed Science, pp. 237–239.
Saltzman, S., Kliger, L., Yaron, B. (1972). “Adsorption-desorption of parathion as affected by soil organic matter.”J. Agric. Food Chem., Vol. 20, pp. 1224–1226.
Wu, C.H., Buehring, N., Davidson, J.M., and Santelmann, P.W. (1975). “Napropamide adsorption, desorption, and movement in soils.”Weed Science, Vol. 23, pp. 454–457.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, YK. Adsorption, desorption and movement of napropamide in soils. KSCE J Civ Eng 8, 619–623 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02823552
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02823552