Abstract
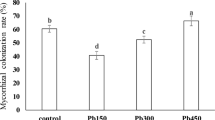
The effect of fulvic acids (FA) on arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi and on the toxicity of lead and manganese toward these symbionts were demonstatedin vitro. Incubation of root segments colonized with the AM fungusGlomus intraradices in undiluted fraction of FA (813 mg/L carbon) decreased an outgrowth of intraradical hyphae. Diluted FA solutions (<271 mg/L C) did not influence the proportion of root segments bearing proliferating hyphae; solution containing 27.1 mg/L C even increased the proliferation. A decrease of heavy metal toxicity toward the fungus was observed when FA (81.3 mg/L C) were added to the solutions containing higher concentrations (≤100 μmol/L) of Mn and Pb; the positive effect of FA was not significant at higher concentrations of metals (0.5 mmol/L). A short-term cultivation of six different saprophytic microorganisms — three actinomycetes and three filamentous fungi — on the FA media (81.3 mg/L C) did not result in a modification of hyphal proliferation from the root segments subsequently incubated in these media.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aso S., Sakai I.: Studies on the physiological effects of humic acid. Part 1. Uptake of humic acid by crop plants and its physiological effects.Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 9, 1–91 (1963).
Avio L., Giovannetti M.: Vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal infection of lucerne roots in a cellulose-amended soil.Plant & Soil 112, 99–104 (1988).
Campbell C.D., Hird M., Lumsdon D.G., Meeussen J.C.L.: The effect of EDTA and fulvic acid on Cd, Zn, and Cu toxicity to a bioluminescent construct (pUSC607) ofEscherichia coli.Chemosphere 40, 319–325 (2000).
Christl I., Kretzschmar R.: Relating ion binding by fulvic and humic acids to chemical composition and molecular size. Part 1. Proton binding.Environ. Sci. Technol. 35, 2505–2511 (2001).
Christl I., Milne C.J., Kinniburgh D.G., Kretzschmar R.: Relating ion binding by fulvic and humic acids to chemical composition and molecular size. Part 2. Metal binding.Environ. Sci. Technol. 35, 2512–2517 (2001).
Diatloff E., Harper S.M., Asher C.J., Smith F.W.: Effects of humic and fulvic acids on the rhizotoxicity of lanthanum and aluminium to corn.Austral. J. Soil. Res. 36, 913–919 (1998).
Douds D.D., Galvez L., Franke-Snyder M., Reider C., Drinkwater L.E.: Effect of compost addition and crop rotation point upon VAM fungi.Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 65, 257–266 (1997).
Führ F., Sauerbeck D.: The uptake of colloidal organic substances by plant roots as shown by experiments with14C-labeled humus compounds, pp. 317–328 inIsotopes in Plant Nutrition and Physiology. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna (Austria) 1967.
Gildon A., Tinker P.B.: Interactions of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal infection and heavy metals in plants. Part I. The effects of heavy metals on the development of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizas.New Phytol. 95, 247–261 (1983).
Gramss G., Ziegenhagen D., Sorge S.: Degradation of soil humic extract by wood- and soil-associated fungi, bacteria, and commercial enzymes.Microb. Ecol. 37, 140–151 (1999).
Gryndler M., Hršelová H., Chvátalová I., Vosátka M.:In vitro proliferation ofGlomus fistulosum intraradical hyphae from mycorrhizal root segments of maize.Mycol. Res. 102, 1067–1073 (1998a).
Gryndler M., Vosátka M., Hršelová H., Chvátalová I., Škrdleta V.: Effect of glucose on the development ofGlomus fistulosum colonization and extraradical mycelium on maize roots.Folia Microbiol. 43, 635–643 (1998b).
Gryndler M., Hršelová H., Vosátka M., Votruba J., Klír J.: Organic fertilization changes the response of mycelium of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and their sporulation to mineral NPK supply.Folia Microbiol. 46, 540–542 (2001).
Joner E.J., Jakobsen I.: Growth and extracellular phosphatase activity of arbuscular mycorrhizal hyphae as influenced by soil organic matter.Soil Biol. Biochem. 27, 1153–1159 (1995).
Kunc F., Lokhmacheva R.A., Macura J.: Biological decomposition of fulvic acid preparations.Folia Microbiol. 21, 257–267 (1976).
Ledin M., Krantz-Rülcker C., Allard B.: Microorganisms as metal sorbents: comparison with other soil constituents in multi-compartment system.Soil Biol. Biochem. 31, 1639–1648 (1999).
Leyval C., Singh B.R., Joner E.J.: Occurrence and infectivity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in some Norwegian soils influenced by heavy metals and soil properties.Water Air Soil Pollut. 84, 203–216 (1995).
Leyval C., Turnau K., Haselwandter K.: Effect of heavy metal pollution on mycorrhizal colonization and function: physiological, ecological and applied aspects.Mycorrhiza 7, 139–153 (1997).
Masciandaro G., Ceccanti B.: Assessing soil quality in different agro-ecosystems through biochemical and chemico-structural properties of humic substances.Soil Till. Res. 51, 129–137 (1999).
McGee P.A.: Alteration of growth ofSolanum opacum andPlantago drummondii and inhibition of regrowth of hyphae of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi from dried root pieces by manganese.Plant & Soil 101, 227–233 (1987).
Ravnskov S., Larsen J., Olsson P.A., Jakobsen I.: Effects of various organic compounds on growth and phosphorus uptake of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus.New Phytol. 141, 517–524 (1999).
Ross S.M.: Retention, transformation and mobility of toxic metals in soils, pp. 63–152 in S.M. Ross (Ed.):Toxic Metals in Soil-Plant Systems. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester (UK) 1994.
Sayed W.F., Mohaowad S.M., Abd El-Karim M.M.: Effect of Al, Co and Pb ions on growth ofFrankia spp. in a mineral medium.Folia Microbiol. 45, 153–156 (2000).
Schnitzer M.: The synthesis, chemical structure, reactions and function of humic substances, pp. 14–28 in R.G. Burns, G. Dell'Agnola, S. Miele, S. Nardi, G. Savoini, M. Schnitzer, P. Sequi, D. Vaughan, S.A. Visser (Eds):Humic Substances, Effect on Soil and Plants. Reda Ramo Editoriale degli Agricoltori, Roma 1986.
Sims J.R., Haby V.A.: Simplified colorimetric determination of soil organic matter.Soil Sci. 112, 137–141 (1971).
Skladany G.J., Metting F.B.: Bioremediation of contaminated soil, pp. 483–513 in F.B. Metting (Ed.):Soil Microbial Ecology. Applications in Agricultural and Environmental Management. Marcel Dekker, New York 1992.
Stevenson F.J.: Gross chemical fractionation of organic matter, pp. 1409–1421 in C.A. Black, D.D. Evans, J.L. White, L.E. Ensminger, F.E. Clark (Eds):Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties. American Society of Agronomy, Madison 1965.
Tan K.H., Nopamornbodi V.: Fulvic acid and the growth of the ectomycorrhizal fungus,Pisolithus tinctorius.Soil Biol. Biochem. 11, 651–653 (1979).
Ullah S.M., Gerzabek M.H.: Influence of fulvic and humic acids on Cu-toxicity and V-toxicity toZea mays (L.).Bodenkultur 42, 123–134 (1991).
Vallini G., Pera A., Avio L., Valdrighi M., Giovannetti M.: Influence of humic acids on laurel growth, associated rhizospheric microorganisms, and mycorrhizal fungi.Biol. Fertil. Soils 16, 1–4 (1993).
Vaughan D.: Effect of humic substances on metabolic processes in plants, pp. 54–77 in R.G. Burns, G. Dell'Agnola, S. Miele, S. Nardi, G. Savoini, M. Schnitzer, P. Sequi, D. Vaughan, S.A. Visser (Eds):Humic Substances, Effect on Soil and Plants. Reda Ramo Editoriale degli Agricoltori, Roma 1986.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malcová, R., Gryndler, M., Hršelová, H. et al. The effect of fulvic acids on the toxicity of lead and manganese to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungusGlomus intraradices . Folia Microbiol 47, 521–526 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02818792
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02818792