Abstract
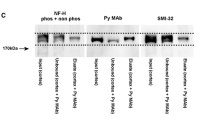
Sera of normal controls and of patients with neurological diseases contain antineurofilament antibodies. Recent studies suggest that biochemically and immunologically distinct subclasses of neurofilaments occur in different types of neurons. Alzheimer's disease (AD), the major cause of dementia, is associated with a marked degeneration of brain cholinergic neurons. In the present work we characterized the repertoire and age dependence of antineurofilament antibodies in normal sera and examined whether the degeneration of cholinergic neurons in AD is associated with serum antibodies directed specifically against the neurofilaments of mammalian cholinergic neurons. This was performed by immunoblot assays utilizing neurofilaments from the purely cholinergic bovine ventral root neurons and from the chemically heterogeneous bovine dorsal root neurons. Antibodies to the heavy neurofilament protein NF-H were detected in normal control sera. Their levels were significantly higher in older (aged 70–79) than in younger (aged 40–59) subjects. These antibodies bound similarly to bovine ventral root and dorsal root NF-H and their NF-H specificity was unchanged during aging. In contrast, the levels of IgG in AD sera that are directed against ventral root cholinergic NF-H were higher than those directed against the chemically heterogeneous dorsal root NF-H. Immunoblot experiments utilizing dephosphorylated ventral root and dorsal root NF-H and chymotryptic fragments of these molecules revealed that AD sera contain a repertoire of antimamalian NF-H IgG. A subpopulation of these antibodies binds to phosphorylated epitopes that are specifically enriched in ventral root cholinergic NF-H and that are located on the carboxy terminal domain of this molecule. The level of these anticholinergic NF-H IgG are significantly higher in AD sera than in those of both normal controls and patients with multi-infarct dementia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steinart D. M. and Roop D. R. (1988)Ann. Rev. Biochem. 57, 593–625.
Robinson P. A. and Anderton B. H. (1988)Rev. Neurosci. 2, 1–41.
Myers M. W., Lazzarini R. A., Lee V. M.-Y., Schlaepfer, W. W., and Nelson D. L. (1987)EMBO J. 6, 1617–1626.
Julien J.-P., Meyer D., Mushynski W., and Grosveld F. (1986) inMolecular Aspects of Neurobiology, Montalcini et al., eds., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 176–181.
Jones S. M. and Williams R. C. (1982)J. Biol. Chem. 257, 9902–9905.
Carden M. J., Schlaepfer W. W., and Lee V. M.-Y. (1985)J. Biol. Chem. 260, 9805–9817.
Julien J.-P. and Mushynski W. E. (1982)J. Biol. Chem. 257, 10,467–10,470.
Berglund A. M. and Ryugo D. K. (1991)J. Comp. Neurol. 306, 393–408.
Campbell N. J. and Morrison J. H. (1989)J. Comp. Neurol. 282, 191–205.
Clark E. A. and Lee, V. M.-Y. (1991)J. Neurosci. Res. 30, 116–123.
Faigon M., Hadas E., Alroy G., Chapman J., Auerbach J. M., and Michaelson D. M. (1991)J. Neurosci. Res. 29, 490–498.
Szaro B. G., Whitnall M. H., and Gainer H. (1990)J. Comp. Neurol. 302, 220–235.
Vickers J. C., Costa M., Vitadello M., Dahl D., and Marotta C. A. (1990)Neuroscience 39, 743–759.
Sotelo J., Gibbs J. R., and Gajdusek D. C. (1980)Science 210, 190–196.
Bahmanyar S., Liem R. K. H., Griffin I. W., and Gajdusek D. C. (1984)J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 43, 369–375.
Toh B., Gibbs C., Gajdusek D. C., Goudsmit J., and Dahl D. (1985)Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 3485–3489.
Kurki P., Helve T., Dahl D., and Virtanen I. (1986)J. Rheumatol. 13, 69–73.
Galbraith G. M. P., Emerson D., Fudenberg H. H., Gibbs C. J., and Gajdusek D. C. (1986)J. Clin. Invest. 78, 865–869.
Brown R. H., Johnson D., Ogonowski M., and Weiner H. L. (1987)Neurology 37, 152–155.
Kumar M., Cohen D., and Eisdorfer C. (1988)Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2, 50–55.
Fudenberg H. H. and Singh V. K. (1988)Drug Dev. Res. 15, 165–174.
Yates C. M., Simpson J., Maloney A. F. J., Gordon A., and Reid A. H. (1980)Lancet 11, 979.
Coyle J. T., Price D. L., and Delong M. R. (1983)Science 219, 1184–1190.
Chapman J., Bachar O., Korczyn A. D., Wertman E., and Michaelson D. M. (1988)J. Neurochem. 51, 479–485.
Chapman J., Bachar O., Korczyn A. D., Wertman E., and Michaelson D. M. (1989)J. Neurosci. 9, 2710–2717.
Hassin-Baer S., Wertman E., Raphael M., Stark V., Chapman, J., and Michaelson D. M. (1992)Neurology 42, 551–555.
Sorenson K. and Brodbeck U. (1986)J. Immunol. Meth. 95, 291–293.
Debus E., Flugge G., Weber K., and Osborn M. (1982)EMBO J. 1, 41–45.
Shaw G., Osborn M., and Weber K. (1986)Eur. J. Cell. Biol. 42, 1–9.
Chin T. K., Eagles P. A. M., and Magg A. (1983)Biochem. J. 215, 239–252.
McKhann G., Drachmann D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., and Stadlan E. M. (1984)Neurology 34, 939–944.
Zemcov A., Barclay L. L., Brush D., and Blass J. P. (1984)J. Am. Geriatric Soc. 32, 801–823.
Berg L. (1984)Br. J. Psychiat. 145, 339–340.
Colton T. (1974)Statistics in Medicine, Little Brown Co., Boston.
Ingram C. R. K., Phegan J., and Blumental H. T. (1974)J. Gerontol. 29, 20–27.
Elizan T. S., Casals J., and Yahr M. D. (1983)J. Neurol. Sci. 59, 341–347.
Sternberger L. A. and Sternberger N. H. (1983)Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80, 6126–6130.
Lee V. M.-Y., Carden M. J., Schlaepfer W. W., and Trojanowski J. Q. (1987)J. Neurosci. 7, 3474–3488.
Dahl D., Labkovsky B, and Bigmani A. (1988)J. Comp. Neurol. 271, 445–450.
Tchernakov K., Soussan L., Hassin-Baer S., Wertman E. and Michaelson D. M. (1993)Res. Immunol. 143, 671–675.
Foley P., Bradford H. F., Dochert M., Fillet H., Levine V. M., McEwen B., Bucht G., and Hardy J. (1988)J. Neurol. 235, 466–471.
McRae A. and Dahlstrom A. (1992)Rev. Neurosci. 3, 79–98.
Sternberger N. H., Sternberger L. A., and Ulrich J. (1985)Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 4274–4276.
Iqbal K. and Grundke-Iqbal I. (1991)Mol. Neurobiol. 5, 399–410.
Lichtenberg-Kraag B., Mandelkow E. M., Biernat J., Steiner B., Schroter C., Gustke N., Meyer H. E., and Mandelkow E. (1992)Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 5384–5388.
Mashiah E., Mallory M., Hansen L., Alford M., Deteresa R., and Terry R. (1993)Am. J. Pathol. 142, 1–13.
Soussan L., Barzilai A., and Michaelson D. M. (1993)J. Neurochem. 62, 770–776.
Chapman J., Alroy G., Weiss Z., Faigon M., Feldon J., and Michaelson D. M. (1991)Neuroscience 40, 297–305.
Dubovik V., Faigon M., Feldon J., and Michaelson D. M. (1993)Neuroscience 56, 75–82.
Eilam D., Szechtman H., Faigon M., Dubovik V., Feldon J., and Michaelson D. M. (1993)Neuroscience 56, 83–91.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soussan, L., Tchernakov, K., Bachar-Lavi, O. et al. Antibodies to different isoforms of the heavy neurofilament protein (NF-H) in normal aging and Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurobiol 9, 83–91 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02816107
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02816107