Abstract
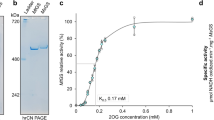
Removal of Mn2+ by EDTA treatment converted dodecameric glutamine synthetase (GS) fromStreptomyces aureofaciens into inactive subunits but did not affect significantly their conformation. However, when fractionated by gel filtration FPLC, the Mn2+-free subunits showed a 7-fold increase ofA 280, probably due to a significant alteration in their tertiary structure. Mn2+ reduced theA 280 of the subunits and promoted their reaggregation to form active GS. Mg2+ or Ca2+ but not Co2+ or Zn2+ might have similar effects. The results suggest that specific divalent cations might play a crucial role in stabilizing subunit interactions as well as the conformation of the individual subunits inStreptomyces GS. The role of specific divalent cations in the regulation of GS turnover is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almassy R.J., Janson C.A., Hamlin R., Xuong N.H., Eisenberg D.: Novel subunit-subunit interactions in the structure of glutamine synthetase.Nature 323, 304–309 (1986).
Chervenka C.H.: Long column meniscus depletion sedimentation equilibrium technique for the analytical ultracentrifuge.Anal. Biochem. 34, 24–29 (1970).
Hames B.D., Rickwood D.:Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins: A Practical Approach. IRL Press, London-Washington (DC) 1981.
Hillemann D., Dammann T., Hillemann A., Wohlleben W.: Genetic and biochemical characterization of the two glutamine synthetases GSI and GSII of the phosphinothricyl-alanyl-alanine producer,Streptomyces viridochromogenes Tu.J. Gen. Microbiol. 139, 1773–1783 (1993).
Kopáček P., Tesařová Z., Miňková Z.: Analysis of urinary proteins by SDS-electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel and immunoblotting. (In Czech)Biochem. Clin. Bohemoslov. 17, 45–55 (1988).
Liaw S.H., Villafranca J.J., Eisenberg D.: A model for oxidative modification of glutamine synthetase, based on crystal structures of mutant H269N and the oxidized enzyme.Biochemistry 32, 7999–8003 (1993).
Matsuoka K., Kimura K.J.: Conformational changes inMycobacterium smegmatis glutamine synthetase induced by certain divalent cations.J. Biochem. 97, 1033–1042 (1985).
Nguyen K.T., Nguyen L.T., Běhal V.: How is glutamine synthetase I activity fromStreptomyces anreofaciens regulated?Biotechnol. Lett. 17, 609–614 1995a).
Nguyen L.T., Nguyen K.T., Kopecký J., Novotná P., Běhal V.: Purification and characterization of novel valine dehydrogenase fromStreptomyces aureofaciens.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1251, 186–190 (1995b).
Rivett A.J.: Preferential degradation of the oxidized modified form of glutamine synthetase by intracellular mammalian proteases.J. Biol. Chem. 260, 300–305 (1985).
Shapiro B.M., Stadtman E.R.: Regulation of glutamine synthetase. IX. Reactivity of the sulfhydryl groups of the enzyme fromEscherichia coli.J. Biol. Chem. 242, 5069–5079 (1967).
Shapiro B.M., Ginsburg A.: Effect of specific divalent cations on some physical and chemical properties of glutamine synthetase fromEscherichia coli. Taut and relaxed enzyme form.Biochemistry 7, 2153–2167 (1968).
Whitaker J.R., Granum P.E.: An absolute method for protein determination based on difference in absorbance at 235 and 280 nm.Anal. Biochem. 109, 156–159 (1980).
Woolfolk C.A., Stadtman E.R.: Regulation of glutamine synthetase. I. Purification and properties of glutamine synthetase fromEscherichia coli.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 122, 174–189 (1967).
Wray L.V. Jr.Fisher S.H.: Cloning and nucleotide sequence of theStreptomyces coelicolor gene encoding glutamine synthetase.Gene 71, 247–256 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, K.T., Nguyen, L.T., Kopecký, J. et al. Removal of Mn2+ induces dissociation of glutamine synthetase fromStreptomyces aureofaciens . Folia Microbiol 42, 539–543 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815461
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815461