Abstract
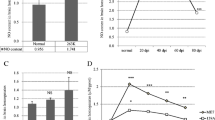
Scrapie is a degenerative disease of the central nervous system of sheep and goats. The causative agent has been passaged to a number of laboratory species, including mice and hamster. Amyloid plaque formation and vacuolation, the signs of senile dementia, are found in the brains of mice infected with 87V scrapie agent. Dopamine (DA) and norepinephrine (NE) concentrations in the brains of scrapie-infected mice were measured with high-performance liquid chromatography-electrochemical detector (HPLC-ECD). A significant decrease in NE level was exhibited in all regions tested, whereas the level of DA decreased significantly only in cerebral cortex. Immunohistochemistry was used to examine immunoreactive catecholamine neurons in substantia nigra and locus ceruleus using antisera against tyrosine hydroxylase (TH). The population of TH-immunoreactive neurons in the substantia nigra and locus ceruleus were significantly decreased in scrapie-infected mice compared to controls. These data suggest that both the noradrenergic and dopaminergic system are sensitive to the action of scrapie agent 87V and that changes in the catecholamine levels in the brains of scrapie-infected mice may contribute to some of the clinical symptoms of the diseases, such as ataxia and apraxia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassant M. H., Fage D., Dedek, F., Cathala L., Court L., and Scatton B. (1984) Monoamine abnormalities in the brain of scrapie-infected rats. Brain Res.308, 182–185.
Beley A., Zekhnini A., Lartillot S., Fage D., and Bralet J. (1987) Improved method for determination of acetylcholine, choline, and other biogenic amines in a single brain tissue sample using high performance liquid chromatography and electrochemical detection.J. Liquid Chromatogr. 10, 2977–2992.
Brozoski T. J., Brown R. M., Rosvold H. E., and Goldman P. S. (1979). Cognitive deficit caused by regional depletion of dopamine in prefrontal cortex of rhesus monkey.Science 205, 929–932.
Bruce M. E., and Dickinson A. G. (1985) Genetic control of amyloid plaque production and incubation period in scrapie-infected mice.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 44, 385–294.
Bruce M. E., Dickinson A. G., and Fraser H. (1976) Cerebral amyloidosis in scrapie in the mouse, effect of agent strain and mouse genotype.Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2, 471–478.
Carp R. I. and Callahan S. M. (1991) Variation in the characteristics of 10 mouse-passaged scrapie lines derived form five scrapie positive sheep.J. Gen. Virol. 72, 293–298.
Carp R. I., Ye X., Kascsak R. J., and Rubenstein R. (1994) The nature of the scrapie agentbiological characteristics of scrapie in different scrapie strain-host combinations, inSlow Infections of the Central Nervous System (Björnsson J., Carp R. I., Löve A., and Wisniewski H. M., eds.), New York Academy of Science, NY, pp. 221–234.
Gajdusek D. C. and Gibbs C. J. (1971) Transmission of two subacute spongiform encephalopathies of man (Kuru and Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease to new world monkeys).Nature 230, 588–591.
Gibson P. H. (1986) Distribution of amyloid plaques in four regions of the brains of mice infected with scrapie by intracerebral and intraperitoneal routes of injection.Acta Neuropathol. (Berl.) 69, 322–325.
Hanson R. P., Eckrode R. J., Marsh R. F., Zu Rhein G. M., Kanitz C. L., and Gustafson D. P. (1971) Susceptibility of mink to, sheep scrapie.Science 172, 859–861.
Jeffrey M., Goodsir C. M., Bruce M. E., McBride P. A., and Farquhar C. (1994) Morphogenesis of amyloid plaques in 87V murine scrapie.Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 20, 535–542.
Kim Y. S., Carp R. I., Callahan S. M., and Wisniewski H. M. (1987) Incubation and survival times for mice injected stereotaxically with three scrapie strains in different brain regions.J. Gen. Virol. 68, 695–702.
Kim Y. S., Carp R. I., Callahan S. M., and Wisniewski H. M. (1990) Incubation periods and histopathological changes in mice injected stereotaxically in different brain areas with the 87V scrapie strain.Acta Neuropathol. (Berl.) 80, 388–392.
Kimberlin R. H. (1984) Scrapie: the disease and the infectious agent.Trends Neurosci. 7, 312–316.
Lindvall D. and Björklund A. (1983( Dopamine and norepinephrine containing neuron systems: Their anatomy in the rat brain, inChemical Neuroanatomy (Emson P. C., ed.), Raven, NY, pp. 229–255.
Moore R. Y. and Bloom F. E. (1979) Central catecholamine neuron systems: Anatomy and physiology of the norepinephrine and epinephrine systems.Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 113–168.
Nazarali A. J. and Reynolds G. P. (1992) Monoamine neurotransmitters and their metabolites in brain regions in Alzheimer’s disease: a postmortem study.Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 12, 581–587.
Prusiner S. B. and Hsiao K. K. (1994) Human prion diseases.Ann. Neurobiol. 35, 385–395.
Quinn M. R., Kim Y. S., Lossinsky A. S., and Carp R. I. (1988) Influence of stereotaxically injected scrapie on transmitter systems of mouse cerebellum.Brain Res. 445, 297–302.
Rohwer R. G., Neckers L. M., Trepel J. B., Gajdusek D. C., and Wyatt R. J. (1981) Serotonin concentrations in brain and blood of scrapie-infected and normal hamsters and mice.Brain Res. 220, 367–371.
Satoh J., Irino M., Martin P. M., Mailman R. B., and Suzuki K. (1991) Neurochemical and immunocytochemical studies of catecholamine system in the brindled mouse.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 50, 793–808.
Wells G. A. H., Scott A. C., Johnson C. T., Gunning R. F., Hancock R. D., Jeffrey M., et al. (1987) A novel progressive spongiform encephalopathy in cattle.Vet. Res. 121, 419–420.
Wisniewski H. M., Wegiel J., and Kozielski R. (1994) Amyloidosis in prion diseases and cells involved in PrP fibrillogenesis, inSlow Infections of the Central Nervous System (Björnsson J., Carp R. I., Löve A., and Wisniewski H. M., eds.), New York Academy of Science, NY, pp. 191–209.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yun, SW., Choi, EK., Ju, WK. et al. Extensive degeneration of catecholaminergic neurons to scrapie agent 87V in the brains of IM mice. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 34, 121–132 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815074
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815074