Summary
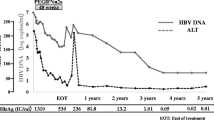
IFN-α was administered intermittently over a 6 month period in 39 patients with chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis confirmed by peritoneoscopy and liver biopsy. Three million units of IFN-α were administered 3 times a week for the first 6 months then twice, then once a week. In 26 patients (67%), GPT decreased and remained within the normal range during the course of administration, and in 9 patients (23%) GPT remained normal for over 6 months after the discontinuation of IFN-α. There was no significant difference of efficacy among 3 groups liver histology groups (CPH, CAH-2A, and CAH-2B), but GPT decreased significantly in patients with sporadic hepatitis compared to patients with a history of blood transfusion. Furthermore, GPT decreased significantly in patients with a history of a blood transfusion within the preceding 2 years compared to patients with a history of a blood transfusion over 7 years ago. GPT increased markedly after an early tapering to 2 doses weekly, but it did not increase after a 6 month administration. In conclusion, the long-term administration of 300 million unit IFN-α, 3 times weekly for 6 months, about 2.5 hundred million units in total, is thought to be an effective way to control chronic NANB hepatitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoofnagle, JH, Mullen KD, Brian Jones D, et al: Treatment of chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis with recombinant human alpha interferon. N Engl J Med 1986;315:1575–1578
Weiland O, Schvarcz R, Wejstal R, et al: Interferon alpha-2b treatment of chronic posttransfusion non-A, non-B hepatitis: Interim results of a randomized controlled open study. Scand J Infect Dis 1989;21:127–132
Kondo T, Hino K, Niwa H: Advances of interferon therapy for chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis. Medical Practice 1990;7:637–643 (in Japanese)
Davis GL, Balart LA, Schiff ER, et al: Treatment of chronic hepatitis C with recombinant interferon-alha. A multicenter randomized, controlled trial. N Engl J Med 1989;321:1501–1506
Fujioka S, Hino K, Fukuhara A, et al: Treatment of chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis: Comparative study of dosage of human interferen-β. Acta Hepatol Jpn 1989;30:516–521 (in Japanese)
Iino S; Interferon therapy for hepatitis C. Kan Tan Sui 1990;20:59–64(in Japanese)
Koga M, Yano M: Treatment of chronis non-A, nonB hepatitis with interferon: Igaku No Ayumi 1989;151:871–876
Schvarcz R, Weiland O, Wejstal R, et al: A randomized controlled open study of interferon alpha-2b treatment of chrnoic non-A, non-B posttransfusion hepatitis: No correlation of outcome to presence of hepatitis C virus antibodies. Scand J Infect Dis 1989;21:617–625
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid (No. 01570396) for Scientific Research from the Japanese Ministry of Education. Science and Culture, and was also supported by Intractable Hepatitis Research Committee, the Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, T., Sue, K., Kakio, T. et al. Long-term intermittent administration of interferon-α in patients with chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis. Gastroenterol Jpn 26, 187–193 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02811079
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02811079