Abstract
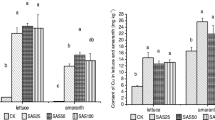
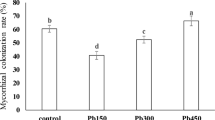
Applying sewage sludges to agricultural land is a widespread practice because of the sludges’ agronomic value as a source of plant nutrients and organic matter. Nevertheless, sludges often contain micropollutants that can constitute a menace for health and the environment. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi are sensitive to sewage sludges that have been spiked, or not, with metallic trace elements (MTE). Here we have investigated if MTE in sewage sludges could be responsible for effects on mycorrhizal development betweenGlomus mosseae andMedicago truncatula. The impact of a dehydrated or composted urban sewage sludge spiked or not with MTE, was tested on spore germination and root colonization byG. mosseae. The sewage sludges depressed both the presymbiotic andin planta stages of development of the mycorrhizal fungus. This negative effect was more related to the metallic pollutant contents of the sludges than to the presence of antagonistic microorganisms or phosphorus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amijee F., Tinker P.B. &Stribley D.P. (1989): The development of endomycorrhizal root systems. VII. A detailed study of effects of soil phosphorus on colonization.New Phytol. 111: 435–446.
Angle J.S. &Heckman J.R. (1986): Effect of soil pH and sewage sludge on VA mycorrhizal infection of soybean.Pl. & Soil 93: 437–441.
Bethlenfalvay G.J. &Linderman R.G. (1992): Mycorrhizae and crop productivity.Amer. Soc. Agric. Special Publ. 54: 1–27.
Cabello M.N. (1997): Hydrocarbon pollution: its effect on native arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF).FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 22: 233–236.
Canarutto S., Petruzzelli G., Lubrano L. &Vigna Guildi G. (1991): How composting affect heavy metal content.Biocycle 32: 48–50.
Daniels-Hetrick B.A. (1984): Ecology of VA mycorrhizal fungi. In:Powell C.L.I. &Bagyaraj D.J. (eds.),VA mycorrhiza, CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp. 35–55.
del Val C., Barea J.M. &Azcon-Aguilar C. (1999): Assessing the tolerance to heavy metals of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi isolated from sewage sludge-contaminated soils.Appl. Soil Ecol. 11: 261–269.
Deneuvy J.P. &Chassande C. (1998): L’épandage des boues de stations d’épuration urbaines: quelle politique et quelle réglementation française pour demain? In: ADEME (ed.),Epandage des boues résiduaires, aspects sanitaires et environnementaux, Actes des Journées Techniques 5 et 6 juin 1997, ADEME Editions, Paris, pp. 48–57.
Dumontet S., Dinel H. &Baloda S.B. (1999): Pathogen reduction in sewage sludge by composting and other biological treatments: A review.Biol. Agric. & Hort. 16: 409–430.
Gianinazzi S. &Schüepp H. (1994):Impact of arbuscular mycorrhizas on sustainable agriculture and natural ecosystems, Birkhäuser-Verlag, Basel.
Giller K.E., Witter E. &McGrath S.P. (1998): Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils.Soil Biol. Biochem. 30: 1389–1414.
Green N.E., Graham S.O. &Schenck N.S. (1976): The influence of pH on the germination of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal spores.Mycologia 68: 929–934.
Griffioen W.A.J., Iestwaart J.H. &Ernst W.H.O. (1994): Mycorrhizal infection of anAgrostis capillaris population on a copper contaminated soil.Pl. & Soil 158: 83–89.
Hepper C. (1983): Effect of phosphate on germination and growth of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi.Trans. Brit. Mycol. Soc. 80: 487–490.
Hewitt E.J. (1966):Sand and water culture methods used in the study of plant nutrition. Technical Communications 22, Ed. 2, revised. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau, London.
IFEN (1999):L’environnement en France. Edition La Découverte, Paris.
Jacquot E., van Tuinen D., Gianinazzi S. &Gianinazzi-Pearson V. (2000): Monitoring species of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in planta and in soil by nested PCR: application to the study of the impact of sewage sludge.Pl. & Soil 226: 179–188.
Jauzein M., Feix I. &Wiart J. (1995):Les micropolluants organiques dans les boues résiduaires des stations d’épuration urbaines. Valorisation agricole des boues d’épuration, connaître pour agir. ADEME Editions, Paris.
Juste C., Chassin P., Gomez A., Linères M., Mocquot B., Feix I. &Wiart J. (1995):Les micropolluants métalliques dans les boues résiduaires des stations d’épuration urbaines. Collection: valorisation agricole des boues d’épuration, connaître pour agir. ADEME Editions, Paris.
Kelly J.J., Haggblom M. &Tate R.L. (1999a): Changes in soil microbial communities over time resulting from one time application of zinc: a laboratory microcosm study.Soil Biol. Biochem. 31: 1455–1465.
Kelly J.J., Haggblom M. &Tate R.L. (1999b): Effects of the land application of sewage sludge on soil heavy metal concentrations and soil microbial communities.Soil Biol. Biochem. 31: 1467–1470.
Legeas M. &Ganere J.P. (1998): Connaissances et acquis: sources, teneurs, nature et devenir des agents pathogènes. In: ADEME (ed.),Epandage des boues résiduaires, aspects sanitaires et environnementaux. Actes des Journées Techniques 5 et 6 juin 1997, ADEME Editions, Paris, pp. 18–22.
Leyval C. &Binet P. (1998): Effect of polyaromatic hydrocarbons in soil on arbuscular mycorrhizal plants.J. Environ. Qual. 27: 402–407.
Leyval C., Turnau K. &Haselwandter K. (1997): Effect of heavy metal pollution on mycorrhizal colonization and function: physiological, ecological and applied aspects.Mycorrhiza 7: 139–153.
Linderman R.G. (1997): Vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal (VAM) fungi. In:Caroll G.C., Tudzynski P., (eds.),The Mycota V part B: Plant relationships, Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, pp. 117–125.
McGrath S.P. &Chaudri A.M. (1999): Long-term effects of metal contamination on Rhizobium.Soil Biol. Biochem. 31: 1205–1207.
McGrath S.P., Chaudri A.M. &Giller E.G. (1995): Long-term effects of metals in sewage sludge on soils, microorganisms and plants.J. Indian Microbiol. 14: 94–104.
Meharg A.A. &Cairney J.W.G. (2000): Co-evolution of mycorrhizal symbionts and their hosts to metal-contaminated environments.Advances Ecol. Res. 30: 69–112.
Miranda J.C.C., Harris P.J. &Wild A. (1989): Effects of soil and plant phosphorus concentrations on vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza in sorghum plants.New Phytol. 112: 405–410.
Nagahashi G., Douds D.D. &Abney G.D. (1996): Phosphorus amendment inhibits hyphal branching of the VAM fungusGigaspora margarita directly and indirectly through its effect on root exudation.Mycorrhiza 6: 403–408.
Philipps J.M. &Hayman D.S. (1970): Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection.Trans. Brit. Mycol. Soc. 55: 158–161.
Pons F. &Gianinazzi-Pearson V. (1984): Effect of phosphorus, potassium, nitrogen and pH on the in vitro behavior of vesicular-arbuscular endomycorrhizal fungi.Cryptog. Mycol. 5: 87–100.
Preston S., Coad N., Towend J., Killham K. &Paton G.I. (2000): Biosensing the acute toxicity of metal interactions: are they additive, synergistic, or antagonistic?Environm. Toxicol. Chem. 19: 775–780.
Sauerbeck D. (1987): Effects of agricultural practices on the physical, chemical and biological properties of soils. Part II Use of sewage sludge and agricultural wastes. In:Barth H. &L’Hermite P. (eds.),Scientific basis for soil protection in the european community, Elsevier Applied Science, London, pp. 181–210.
Schultz R. &Römheld V. (1997): Recycling of municipal and industrial organic wastes in agriculture: Benefits, limitations, and means of improvement.Soil Sci. Pl. Nutr. 43: 1051–1056.
Sommers L.E. (1977): Chemical composition of sewage sludges and analysis of their potential use as fertilizers.J. Environm. Qual. 6: 225–232.
Trouvelot A., Kough J.L. &Gianinazzi-Pearson V. (1986): Mesure du taux de mycorrhization VA d’un système radiculaire. Recherche de méthodes d’estimation ayant une signification fonctionnelle. In:Gianinazzi-Pearson V. &Gianinazzi S. (eds.),Mycorrhizae: Physiology and Genetics, INRA Press, Paris, pp. 217–221.
Weissenhorn I. &Leyval C. (1996): Spore germination of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in soils differing in heavy metal content and other parameters.Eur. J. Soil Biol. 32: 165–172.
Wetzel A. &Werner D. (1995). Ecotoxicological evaluation of contaminated soil using the legume root nodule symbiosis as effect parameter.Environ. Toxicol. Water Qual. 10: 127–133.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacquot-Plumey, E., Caussanel, JP., Gianinazzi, S. et al. Heavy metals in sewage sludges contribute to their adverse effects on the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungusGlomus mosseae . Folia Geobot 38, 167–176 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02803149
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02803149