Abstract
In order to better understand the relative importance of various sources of lead in childhood lead poisoning, high-precision, isotoperatio, solid-source-mass spectrometry of microgram-sized lead samples was applied to three hospitalized cases in Boston, ranging in age from 1.5 to 14 yr, that had blood-lead levels of 0.7–1.2 μg/g. The lead isotopes in the ambient Boston environment (air, soil, and dust) were also measured.
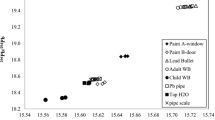
In each case, the isotopic composition (IC) of the child's blood lead was identical with the IC of lead paint taken from the child's residence at a site accessible to the child. Fecal lead samples were also identical to that particular paint. Soil lead IC did not always match the IC of local paints. Paint samples vary widely in their IC's (206/204=17.5–19.4, about 200 times analytical reliability). Dust in homes that never had lead paint contained lead that resembled lead in urban soils. Dust lead IC did not necessarily have the same IC as current automobile lead emissions, but appeared to reflect the long-term accumulation of several sources of urban lead fallout.
Limitations and implications of this data are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. B. Rabinowitz and G. W. Wetherill,Environ. Sci. Tech. 6, 705 (1972).
M. B. Rabinowitz, G. W. Wetherill, and J. D. Kopple,J. Lab. Clin. Med. 90, 238 (1977).
S. Facchetti and F. Geiss,Isotopic Lead Experiment: Status Report. Community of European Communities, Luxembourg, Pub. # EUR 8352 EN, 1982.
W. Manton,Arch. Environ. Health. 32, 149 (1977).
Y. Yaffe, C. Flessel, J. Wesolowski, A. Del Rosario, G. Guirguis, V. Matias, T. DeGarmo, G. Coleman, J. Gramlich, and W. Kelly,Arch. Environ. Health. 38, 237 (1983).
M. B. Rabinowitz, A. Leviton, H. L. Needleman, D. C. Bellinger, and C. Waternaux,Environ. Res. 38, 96 (1985).
G. Tilton, C. Patterson, H. Brown, M. Inghram, R. Hayden, D. Hess, and E. Larsen,Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 66, 1131 (1955).
C. C. Patterson,Geochem. Cosmochem. Acta 47, 1166 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabinowitz, M.B. Stable isotope mass spectrometry in childhood lead poisoning. Biol Trace Elem Res 12, 223–229 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02796682
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02796682