Abstract
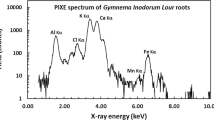
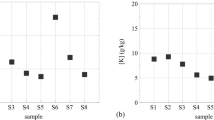
Proton-induced X-ray emission (PIXE) method was employed to study the concentration of heavy elements in betel leaves, betel nuts, and mineral lime consumed in Bangladesh. The samples were collected from different parts of Bangladesh and analyzed by the thicktarget external beam technique of the PIXE method. The samples were exposed to the proton beam as 1-mm thick pellets and irradiated with 2.0-MeV protons having 20-nA beam intensity. The concentration of some 15 elements (K, Ca, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, Se, Br, Rb, Sr, and Pb) was measured by comparison with a calibration curve constructed from the NBS orchard leaf standard SRM 1571. The validity of the procedure has been established by comparative measurements of Cu and Zn with atomic absorption spectrophotometry. The significance of the results is discussed in view of their implications in health and disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. J. Underwood,Trace Elements in Human and Animal Nutrition, 4th ed; Academic, New York, NY, 1977.
A. S. Prasad (Ed.),Trace Elements in Human Health and Disease, Academic, New York, NY, vol. 1 and II, 1976.
Toxicology of Metals, vol. II, US Environmental Protection Agency, Las Vegas, NV, EPA 600/1-77-022, May, 1977.
M. Abdullah, B. Nair, and R. K. Chandra (eds.), Proc. Int. Symp. on Health Effects and Interactions of Essential and Toxic Elements, Lund, Sweden, 1984.
WHO Tech. Report No. 276 on Prevention of Cancer, WHO Scientific Group, Genera, 1964.
D. A. Hadi, M. Ali, S. K. Biswas, M. M. Islam, and A. H. Khan,Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 35, 793 (1984).
B. Martin (ed.),Proc. Third Int. Conf. on Particle-Induced X-ray Emission and its Analytical Applications. Heidelberg, FRG, July 18–22, 1983 [Supplement toNuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research,B3 (1984)].
A. H. Khan, M. Khaliquzzaman, M. B. Zaman, M. Hussain, M. Abdullah, and S. Akhter,J. Radioanal. Chem. 53, 157 (1980).
M. Khaliquzzaman, M. B. Zaman and A. H. Khan,Nucl. Instr. Meth. 181, 209 (1981).
S. K. Biswas, M. Khaliquzzaman, M. M. Islam, and A. H. Khan,Nucl. Inst. Meth. B3, 337 (1984).
D. D. Hamphill,Ann. NY Acad Sci. 199, 46 (1972).
P.R. Kamath, I. S. Bhat, A. A. Khan, and A. K. Ganguly,Proc. 1st. Int. Cong. of Radiation Protection, Rome, Italy, September, 1966.
G. Mueller,Chemiker-Zeitung 103, 33 (1976).
R. R. Brooks and J. M. Trow,NZ J. Sci. 22, 289 (1979).
A. S. Prasad (Ed.),Trace Elements in Human Health and Disease, Academic, New York, NY, vol. II, 1976.
E. L. Cole and T. Zingaro,Assoc. Publ. Analysts 12, 68 (1974).
World Health Organization,Tech. Rept. Sr. No. 502, WHO Scientific Group, Genera, 1972.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tarafdar, S.A., Akhter, S., Kar, S. et al. Multielement proton-induced X-ray emission analysis of betel leaves, betel nuts, and lime. Biol Trace Elem Res 12, 121–131 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02796670
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02796670