Abstract
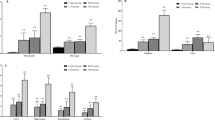
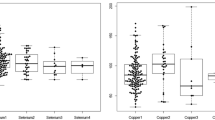
Reye’s syndrome (Rs) is an acute illness in children manifested by encephalopathy and fatty degeneration of the liver. The syndrome may be secondary to injury of mitochondria following a toxic insult in a susceptible individual with a viral illness. Since the response to infection often involves a change in trace metals, we investigated the metal status of patients with Rs. Decreased levels of serum and liver selenium (Se) and copper (Cu) were demonstrated via PIXE analysis, in addition to an increase in serum iron (Fe) and zinc (Zn). In a subsequent study using a rat animal model of Rs, the hepatotoxin 4-pentenoic acid (4-PA) produced similar changes in serum and liver trace metals. Serum and liver Se levels were also significantly depleted in rats exposed to another toxin, valproic acid (VPA). Aspirin, known to complex metals, may also be associated with Rs. Rats chronically exposed to aspirin had decreased serum Se, Fe, and Zn compared to controls. Selenium was also decreased in liver, as was Cu. Atomic absorption spectrophotometric analysis of serum and liver Cu for mice exposed to aspirin and influenza A virus were also studied. In liver, Cu was significantly decreased in mice on Cu-deficient diets but, not in control mice exposed to virus, or aspirin and virus. For the Se-deficient animals, liver Cu was not different from controls, but there was an increase in tissue Cu for Se-sufficient mice exposed to virus and aspirin; Cu levels were decreased in sera of this latter group. Serum Cu was increased in Cu-sufficient mice exposed to virus and aspirin. The above data are of biologic and toxicologic interest because of metalloenzyme localization in the mitochondrial matrix, the cellular compartment showing the greatest degree of pathologic change in Rs. In particular, Se-dependent gluthathione peroxidase is a major deterent of peroxidative damage of lipid membranes. The accumulated evidence suggests that alteration of trace metals, e.g., decrease in Se, may promote peroxidation of mitochondrial membranes in patients with Rs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. D. K. Reye, G. Morgan, and J. Baral,Lancet II, 749 (1963).
J. C. Partin, W. K. Schubert, and J. S. Partin,N. Engl. J. Med. 285, 1339 (1971).
A. M. Glasgow and H. P. Chase,Pediat. Res. 9, 133 (1975).
R. E. Braun and D. T. Forman,CRC Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 17, 247 (1982).
W. Maenhaut, L. DeReu, H. A. Van Rinsvelt, J. Cafmeyer, and P. Van Espen,Nucl. Inst. Methods. 168, 557 (1980).
P. Van Espen, H. Nullen, and W. Maenhaut, inMicrobeam Analysis, vol. 1, D. E. Newberry, ed., San Francisco Press, San Francisco, CA, 1979, p. 265.
R. W. Hurd, H. A. Van Rinsvelt, E. A. Perry, J. W. Kondoro, J. M. Andres, J. P. Mickle, B. J. Wilder, W. Maenhaut, and L. DeReu,IEEE Transact. Nucl. Sci. 2, 1319 (1983).
H. A. Van Rinsvelt, R. W. Hurd, J. W. Kondoro, J. M. Andres, and J. P. Mickle,Nucl. Inst. Methods. Physics. Res. IV, 337 (1984).
H. A. Van Rinsvelt, R. Sater, R. W. Hurd, and J. M. Andres,Nucl. Inst. Methods (1985), in press.
P. B. Mortensen, N. Gregerson, S. Kolvraa, and E. Christensen,Biochem. Med. 24, 153 (1980).
P. L. Ogburn, Jr., H. Sharp, J. D. Lloyd-Still, S. P. Johnson, and R. T. Holman,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79, 908 (1982).
L. Flohe and R. Zimmermann,Biochem. Biophys. Acta 223, 210 (1970).
V. A. Fulginiti (Chairman, Committee on Infectious Diseases).Pediatrics 69, 810 (1982).
G. Kolata,Science 227, 391 (1985).
R. C. Bearse, D. A. Close, J. J. Malanify, and C. J. Umbarger,Anal. Chem.,46, 499 (1974).
R. S. Pekarek, G. A. Burghen, and P. J. Bartelloni,J. Lab. Clin. Med. 76, 293 (1970).
J. H. Menna, J. R. J. Sorenson, O. D. Timmons, D. E. Wennerstrom, and L. W. Chang,J. Natl. Reye’s Syndr. Fnd. 3, 31 (1982).
L. Flohe, W. A. Gunzter, and G. Loschen, inTrace Metals in Health and Disease, vol. 1, N. Kharasch, ed., Raven, New York, NY, 1979, p. 263.
H. Sies and K. M. Moss,Eur. J. Biochem.,84, 377 (1978).
H. R. Lotscher, K. H. Winterhalter, E. Carafoli, and C. Richten,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76, 4340 (1979).
I. Lombeck, K. Kasperek, H. D. Harbisch, L. E. Feinendegen, and H. J. Bremer,Eur. J. Pediat. 125, 21 (1977).
G. A. Hazelton and C. A. Lang,Biochem. J. 122, 25 (1980).
J. R. Aprille,Science 197, 908 (1977).
J. C. Partin, J. S. Partin, W. R. Schubert, and R. L. McLauren,J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 34, 425 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andres, J.M., Hurd, R.W. & Van Rinsvelt, H.A. Application of trace metal analysis to basic problems in neurobiology studies of patients with Reye’s syndrome. Biol Trace Elem Res 13, 55–67 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02796621
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02796621