Abstract
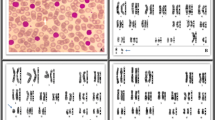
We report a case of a boy with acute lymphoblastic leukemia expressing granular inclusions in the cytoplasm of blastic cells. Granular lymphoblasts had mostly L2 morphology but azurophilic granules were also present in part of the cells with L3 morphology. Immunophenotyping clearly indicated a lymphoid origin of the blasts and showed positivity of HLA-DR, CD10, CD19 and CD24 markers. Cytogenetic analysis brough normal karyotype 46 XY. Molecular genetic analysis showed immunoglobulin heavy chain rearrangement (IgH R/R) and T-cell receptor gamma rearrangement pattern (TCR-gamma C/R). TCR-beta and TCR-delta did not show rearrangements. The course of the disease was favourable. The patient achieved initial complete remission within 4 weeks of protocolar treatment and the remission remains until now, 5 years from the diagnosis and three years after finishing the treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babušiková Oet al. Leukemia-associated marker combinations in acute leukemia suitable for detection of minimal residual disease.Neoplasma: 1993;40: 275–281.
Panzer-Grünmayer ERet al. Characterization of CD7+, CD19+_lymphoid cells after Epstein-Barr virus transformation.J Immunol: 1993;151: 92–99.
Schwarzinger Iet al. Hypergranular acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Report of a case and review of the literature.Ann Hematol: 1993;67: 301–303.
Cantú-Rajmondi Aet al. Biological and clinical features of acute lymphoblastic leukemia with cytoplasmatic granules or inclusions: description of eight cases.Brit J Haematol; 1989;73: 309–314.
Cerezo Let al. Laboratory correlates and prognostic significance of granular acute lymphoblastic leukemia in childrens: a pediatric oncology group study.Am J Clin Pathol: 1991;95: 526–531.
Darbyshire PL, Lilleyman JS. Granular acute lymphoblastic leukemia of children: a morphological phenomenon.J Clin Pathol: 1987;40: 251–253.
Hay CRMet al. Granular common acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults: a morphologic study.Eur J Haematol: 1987;39: 299–305.
Grogan TM, Insalaco SJ, Savage RA, Vail ML. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia with prominent azurophilic granulation and punctate acidic nonspecific esterase and phosphatase activity.Am J Clin Pathol: 1981;81: 716–722.
Yanagira ET, Naeim F, Gale RP, Austin G, Waismann J. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia with giant intracytoplasmatic inclusions.Am J Clin Pathol: 1980;74: 345–349.
Smith H, Collins RJ, Siskind V. Peculiar cytoplasmic inclusions in cells of acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Am J Clin Pathol: 1986;86: 261–263.
Takemori N, Saito N, Marioka M, Sakurada K, Miyazaki T. Peculiar cytoplasmic inclusion in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: cytochemical and electronmicroscopic observation.Am J Pathol: 1985;83: 527–534.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cáp, J., Babušíková, O., Kaiserová, E. et al. Granular acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a 15-year-old boy. Med Oncol 17, 144–146 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02796210
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02796210